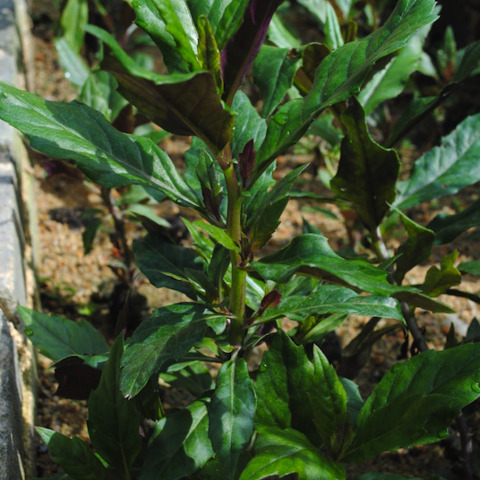
Herbs, perennial. Stems erect, 50-100 cm tall, glabrous, flaccid, rather woody at base, corymbosely branched in upper part, striate when dry. Leaves petiolate or subsessile; blade abaxially becoming purplish when dry, adaxially green, obovate or oblanceolate, rarely oblong-lanceolate, both surfaces glabrous, lateral veins 7-9-paired, curved, base gradually attenuate into winged petioles or subsessile, ± expanded, but not auriculate, margin irregularly repand-dentate or mucronulate, rarely pinnatifid near base. Upper leaves shortly petiolate or subsessile, lanceolate to linear-lanceolate, small. Capitula numerous, ca. 10 mm in diam., in terminal lax corymbs; peduncles 3-4 cm, slender, with 1 or 2(or 3) filiform bracts. Involucres campanulate, 11-15 × 8-10 mm; bracts of calyculus 7-9, linear; phyllaries 13, linear-lanceolate, 11-15 × 0.9-1.5(-2) mm, glabrous, conspicuously 3-ribbed, margin scarious, apically acute or acuminate. Florets orange to reddish; corolla distinctly exceeding involucres, 13-15 mm; tube 10-12 mm, slender; lobes ovate-triangular. Anthers rounded at base, or slightly acute. Style branch tips subulate, papillose. Achenes brownish, cylindric, ca. 4 mm, glabrous, 10-15-ribbed. Pappus white, silky, easily deciduous. Fl. May-Oct.
More
A herb. It keeps growing from year to year It can be scrambling or erect. It grows 35 cm long. The leaves often have no leaf stalks. The leaf blades are broadly oval and 8-15 cm long. They are usually green on top and purple underneath. They are fleshy. They can have teeth or lobes. The flowers are in loose clusters or 4-13 flower heads. They have purple tips.