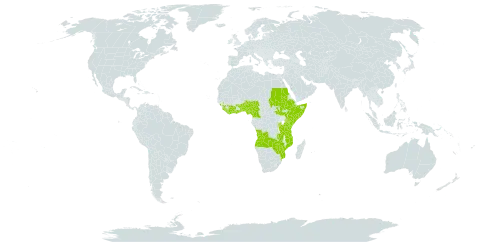
A shrub or small tree. It keeps its leaves throughout the year. It can be climbing. It grows 6 m high The larger branches have thorns 2 cm long. These are on cone shaped corky growths. The branches are long and flexible. The leaves are alternate and compound. They have 2-7 pairs of leaflets and one at the end. The leaves are 25 cm long. The leaflets are almost round and 1-9 cm long by 1-4 cm wide. They are unequal at the base. There can be teeth along the edge. The flowers contain both sexes. They are grouped on shoots 2-14 cm long in the axils of leaves or at the ends of branches. The fruit have 4-8 lobes and are a berry. They are 4-9 mm across. They turn red or black when ripe. They are fleshy and have 4-8 seeds.
Leaves 5–25 cm. long, variable in shape, size and indumentum, with 3–6 pairs of subopposite leaflets, pubescent to glabrous; midribs and petioles with wings up to 3 mm. across; leaflets sessile at constrictions in the wing; lamina 0·7–7 × 0·5–3 cm., elliptic to broadly obovate, apex subacute to rounded, margins usually crenate-serrate to crenate (crenations sometimes very few), base (and more rarely the whole margin) entire, narrowly cuneate, asymmetric.
Small tree or shrub, sometimes scandent, 2–10 m. tall; bark of trunk and larger branches corky, pale brown, often with conical corky bosses up to 2 cm. tall surmounted at least at first by a prickle; smaller branches 4: prickly or unarmed, pubescent to ± glabrous; prickles up to 5 mm. long, pubescent to glabrous, slightly recurved, most often paired in the stipular position; pubescence of simple hairs.
Stamens c. 3 mm. long, inserted at the base of the disk; filaments 2–2·5 mm. long, glabrous, filiform, with a pubescent scale attached by the base to their inner faces; anthers 1 mm. long.
Inflorescences 5–15 cm. long, laxly paniculate, pubescent, often leafy in the lower part, the leaves rapidly grading upwards into oblong foliose bracts and then to minute caducous bracts.
Petals white to yellow, 4–5 mm. long, spreading, pubescent outside, glabrous within, lanceolate.
Calyx-lobes c. 1 mm. long, spreading, ovate, pubescent outside, glabrous within.
Ripe fruits bright red, c. 10 mm. in diam., glabrous, fleshy.
Ovary glabrous; styles c. 2 mm. long, usually pubescent.
Disk c. 1·5 mm. in diam., inconspicuous, pulviniform.
The leaves often with paired thorns at the base
A shrub, or small tree up to 30 ft. high
Branches sometimes long and sarmentose
Erect panicles of small white flowers