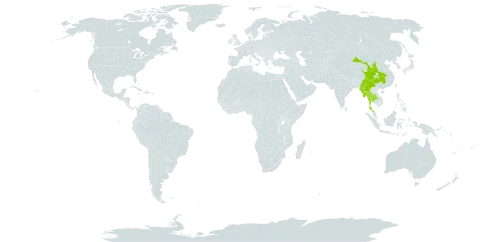
A shrub which can lose its leaves. It grows about 3 m tall. The leaves are large and rich green. Male and female flowers are on separate plants. The leaves are alternate and have teeth. The flowers appear on the leaves. The fruit is fleshy.
| Life form | perennial | ||||||||||||
| Growth form | shrub | ||||||||||||
| Growth support | free-standing | ||||||||||||
| Foliage retention | evergreen | ||||||||||||
| Sexuality | dioecy | ||||||||||||
| Pollination | - | ||||||||||||
| Spread | - | ||||||||||||
| Mature width (meter) | 1.0 - 1.5 | ||||||||||||
| Mature height (meter) | 1.5 - 1.75 | ||||||||||||
| Root system | - | ||||||||||||
| Rooting depth (meter) | - | ||||||||||||
| Root diameter (meter) | - | ||||||||||||
| Flower color | |||||||||||||
| Blooming months |
|
||||||||||||
| Fruit color | |||||||||||||
| Fruiting months |
|
||||||||||||
| Nitrogen fixer | - | ||||||||||||
| Photosynthetic pathway | - |
| Light |
|
| Soil humidity | |
| Soil texture | |
| Soil acidity | |
| Soil nutriment | - |
| Hardiness (USDA) |
| Uses | medicinal |
| Edible | flowers leaves |
| Therapeutic use | - |
| Human toxicity | - |
| Animal toxicity | - |
| Mode | cuttings seedlings suckers |
| Germination duration (days) | - |
| Germination temperacture (C°) | - |
| Germination luminosity | - |
| Germination treatment | - |
| Minimum temperature (C°) | -12 |
| Optimum temperature (C°) | - |
| Size | - |
| Vigor | - |
| Productivity | - |

| LSID | urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:90833-1 |
| WFO ID | wfo-0000981192 |
| COL ID | 3KK67 |
| BDTFX ID | - |
| INPN ID | - |
| Wikipedia (EN) | Link |
| Wikipedia (FR) |