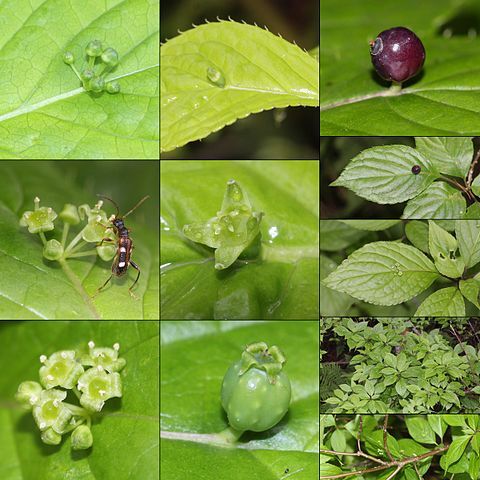
Shrubs 1–2 m tall, deciduous; bark dark brown or grayish black, smooth; young branches green, glabrous, smooth, with conspicuous leaf scars. Leaf petiole 1–5(–6) cm; stipules threadlike, divided apically or rarely undivided; leaf blade abaxially light green, grayish white, or glaucous green, ovate, obovate-elliptic, ovate-rounded, rarely elliptic or ovate lanceolate, 3.5–9(–18) × 2–6(–8.5) cm, papery, glabrous, veins 5–7(or 8), conspicuous, raised abaxially, slightly impressed adaxially, base broadly cuneate or ± rounded, margin spiculate serrate to spiculate crenate, apex acuminate, rarely caudate-acuminate. Umbels between middle and lower 1/3 of midvein, rarely on upper part of young branches; staminate umbels 3–12(–18)-flowered; carpellate umbels 1–3-flowered. Flowers pedicellate. Petals light green, 1–5 mm. Carpellate flowers: style 3–5-divided. Fruit subglobose or ellipsoid, ca. 4–8 mm in diam., nearly sessile. Seeds 3–5, lobes 3–5. Fl. Apr–May, fr. Aug–Oct.
More
A shrub which loses its leaves. It grows 1-3 m tall and spreads 1.5 m wide. Male and female flowers are on separate plants. The leaves are narrowly oval and olive green. The leaves are alternate and have teeth. The flowers appear on the leaves. The male plants have 12 small greenish-white star shaped flowers. Female flowers occur singly. The fruit is fleshy. It is black. The fruit are on the surface of the leaves.
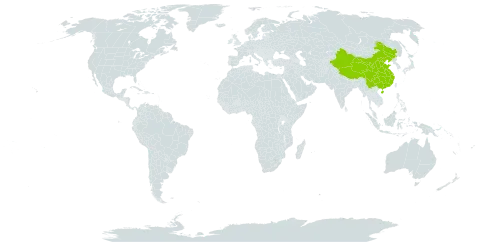
Woods and thickets in hills and low mountains of Japan. Moist rich soil in woods, thickets, valleys, streamsides and roadsides at elevations of 100-3400 metres.
More
It is a temperate plant. They do best in the sun. They need moist soil. It suits hardiness zones 8-9.