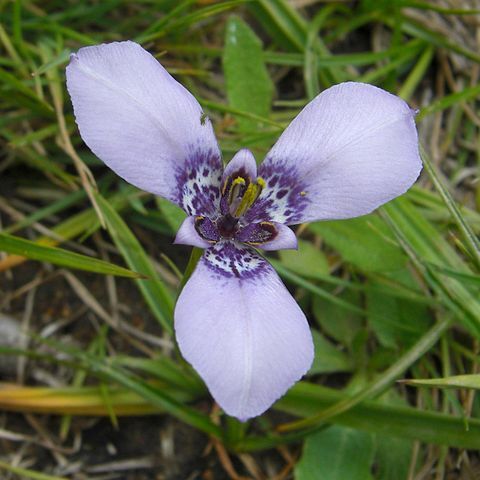
Small perennial herbs with annual leaves and flowers. Rootstock a bulb. Leaves basal, linear, plicate. Stem erect, simple or branched, with reduced sheathing leaves. Spathes herbaceous; apices acute, scarious. Flowers few, blue to violet. Sepals and petals free, the sepals clawed, spreading, far exceeding petals. Stamens monadelphous, erect; anthers spreading, exceeding style branches. Style erect, terete, trifid at top of filament tube; branches appressed to anthers, channelled, bifid near apices; stigmas 6, terminal.