Small tree to 15 m with airy crown and bole to 20 cm diam. but usually much smaller. Bark dark brown, lenticellate to grey and weakly cracking into irregular rectangles; inner bark whitish. Young twigs very dark brown to blackish, lenticellate, leafy ones c. 4–7 mm diam. All foliage and inflorescences in current flush. Leaves to 50 cm long, (l–)3–5(–6)-jugate; petiole 5–15 cm, terete; leaflets 4.5–20 by 2–7.5 cm, ovate-oblong, articulated at petiolule apices, adaxial surface glabrous, shining, abaxial glabrous to hairy, glaucous; base asymmetric, rounded to acute; apex acuminate; veins 5–8 on each side, looping together but not reaching margin. Inflorescences foamy subcorymbose cymes to 50 cm across, axillary, peduncle over half as long, with 3–7 pairs of decussate branches, each with l–3(–4) orders of branchlets; bracts small, caducous. Flowers scented; pedicels c. 1.5–2 mm, each with 2 small persistent bracteoles. Calyx c. 1 mm high, pale pink, lobes broadly triangular, apices rounded to acuminate, often hairy without, margin sometimes ciliate. Petals oblong, c 0.7–1 mm wide, acute, often hairy without, white to pink or cream, margin sometimes ciliate. Filaments 8 or 10 (14) alternately long and short, adaxially strigose, sometimes puberulous abaxially, pink; anthers c. 1 mm, ovate, apiculate, ± glabrous, bright yellow, inserted between 2 linear acute glabrous teeth. Disk fleshy. Ovary glabrous. Capsule c. 1–2 cm diam., globose, pink. Seed 1, ovoid, almost covered in a white aril, testa dark brown, dangling from long funicie (Ashton).
More
Trees 5-10 m tall. Old branches glabrous, young parts yellow pubescent, black or dark brown when dry, with sparse lenticels. Leaves alternate, usually 20-36 cm; rachis cylindric or ridged, glabrous; leaflets 7 or 9, opposite; leaflet blades lanceolate, ovate, or oblong-elliptic, (5-)8-16 × (2.5-)3.5-5(-7) cm, membranous, abaxially pale and glabrous or yellow pubescent, adaxially glabrous, secondary veins 8-12 on each side of midvein, base oblique, margin entire, apex acuminate. Thyrses axillary, slightly shorter than leaves; peduncle pubescent. Flowers 3-4 mm. Pedicel ± as long as flowers, thin, pubescent or glabrous. Calyx 4-or 5-lobed; lobes orbicular to obtusely triangular, outside pubescent or glabrous. Petals 4 or 5, white or creamy white, oblong-elliptic, outside pubescent or glabrous. Filament tube 10-parted to below middle, pubescent or glabrous, segments inside covered with hard trichomes, tips 2-cleft; anthers 8-10, inserted between 2 lobes of filament tips. Ovary spherical, glabrous; style ± as long as filament tube; stigma spherical, tip 2-cleft. Capsule ellipsoid and with a carpopodium, (1.5-)2.5-3 × 1-2.5 cm, glabrous, 1-seeded. Seed black when dry, with a white aril. Fl. Apr-Jun, fr. May-Jun and Nov-Dec.
A tree. It grows 10-20 m tall. The trunk can be 25 cm across. The leaves are alternate and oval. They are 8-16 cm long by 4-5 cm wide. They have opposite leaflets. The flowers are yellowish white and in panicles. The fruit is an oval capsule 3 cm long by 1-3 cm wide. It is red. There is one seed.
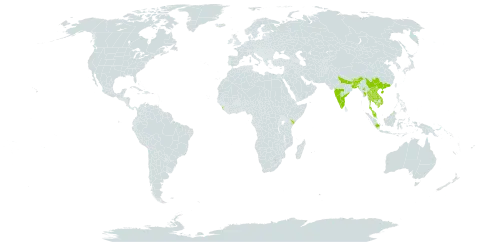
A tropical plant. It grows in Madya Pradesh in India. In southern China it grows in forests between 200-1,300 m above sea level. In Indonesia it grows between 700-2,400 m above sea level.
More
Forests in hilly regions; at elevations from 200-1,300 metres in southern China. Open areas in hill evergreen forest.
UsesLong cultivated in Java, this is an extremely handsome tree suitable for town gardens (cf. Corner, 1940, 1988); it is cultivated under glass in Europe. Its leaves and bark are bitter and of medicinal value; the seeds are allegedly poisonous to some birds.
More
The fruit are sour but eaten. Caution: It may have some poisonous effects. The seeds are probably poisonous.