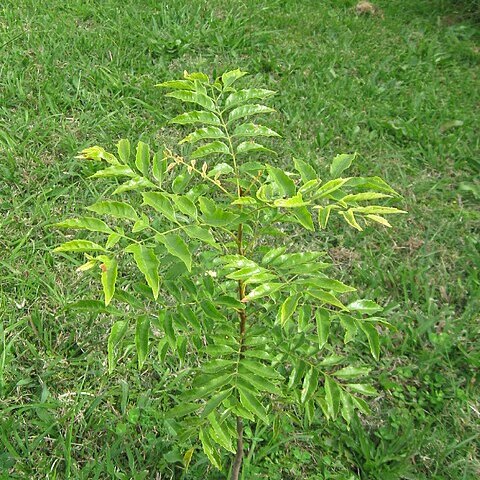
Trees, often ± pachycaulous, or shrubs, monoecious. Indumentum of solitary simple hairs; no glandular scales. Twigs often strongly ribbed, with a thick pith and a very thin wood cylinder; terminal bud protected by bud scales. Leaves often verticillate, sometimes opposite or spirally arranged, paripinnate, 4-40-jugate, without pseudo-stipules; petiole base swollen and beneath deeply 3-lobed, leaving a very characteristic scar, neither petiole nor rachis winged. Leaflets alternate to opposite, below with naked glands; base at the basiscopic side narrow, cuneate, at the acroscopic side broad and rounded; margin serrate to dentate (entire in an Australian variety of J, pseudorhus); midrib prom-nent above, nerves and veins raised on both sides, nerves ending in the marginal teeth. Inflorescences in the axils of bracts or normal leaves, together pseudoterminal, thyrses. Flowers unisexual, monoecious, regular. Sepals 5, slightly connate at base, narrowly imbricate, all equal, margin sometimes slightly petaloid, outside hairy, the margin (partly glandular) ciliolate, inside slightly hairy to glabrous, entire, in fruit persistent and slightly reflexed. Petals 5, as long as or slightly longer than the calyx, shortly clawed to sessile, glabrous or outside at the base and sometimes in the centre, and along the margin slightly hairy, entire, inside either auricled or with two, sometimes with one, erect woolly scale(s), exceptionally (an Australian subspecies of J. javanica) with a crest. Disc entire, lobed, without appendages, glabrous. Stamens 8 (7-10), in male flowers exserted, spreading; filaments at least slightly hairy at base (to completely hairy); anthers obovate, ciliate (or glabrous). Ovary sessile, hairy, 3-locular; style apical, about as long as the ovary, hairy, with 3 swollen stigmatic lines. Ovules 1 per locule. Fruits sessile, loculicidal, slightly warty, densely pilose with stiff, irritating hairs, inside also densely pilose. Seeds with a swollen annular sarcotesta around the hilum.
More
Monoecious or dioecious trees with saponin in bark, leaves and pericarp. Leaves paripinnate; leaflets opposite to alternate, usually serrate, semicoriaceous, usually pellucid-punctate. Inflorescence axillary or ramiflorous, usually panicle-like; cymules stalked. Flowers small, regular. Calyx deeply 5-lobed, lobes ovate. Petals 5, ovate, obovate or suborbicular, clawed; scales 2, broad, crested. Disc complete, glabrous. Stamens 7–10; filaments hairy. Ovary sessile, 3-or 4-locular; ovule 1 per locule; style short. Fruit usually obovoid, 3-or 4-locular, loculicidally dehiscent; valves woody, verrucose, rusty-setose outside, villous inside. Seed obovoid, with small basal cupular aril. [Editorial note, 17 August 2020: this genus description from Reynolds (1985: 67) requires revision since it included Jagera discolor in the Flora of Australia Volume 25 Jagera treatment which is now treated as a synonym of Cnesmocarpon dasyantha.]