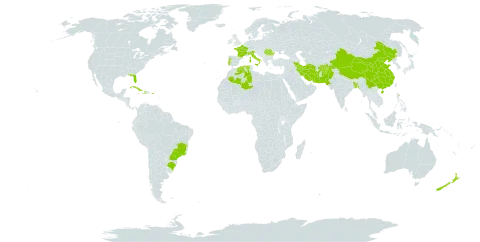
| Therapeutic use
|
Antineoplastic agents (aerial part), Hypotension (aerial part), Hair loss (flower), Anesthesia (flower), Antifungal agents (flower), Antineoplastic agents (flower), Astringents (flower), Callosities (flower), Contraceptive agents (flower), Dandruff (flower), Diabetes mellitus (flower), Ear diseases (flower), Exanthema (flower), Eye diseases (flower), Headache (flower), Heart diseases (flower), Hoarseness (flower), Hypnotics and sedatives (flower), Liver diseases (flower), Oral ulcer (flower), Pain (flower), Scorpion stings (flower), Skin diseases (flower), Thirst (flower), Vision disorders (flower), Anticonvulsants (fruit), Tetanus (fruit), Antifungal agents (leaf), Callosities (leaf), Dysmenorrhea (leaf), Earache (leaf), Eye diseases (leaf), Hematologic diseases (leaf), Hemorrhage (leaf), Hemorrhoids (leaf), Leprosy (leaf), Mastitis (leaf), Oral ulcer (leaf), Otitis (leaf), Anti-poisoning (leaf), Skin diseases (leaf), Stomatitis (leaf), Suppuration (leaf), Ulcer (leaf), Disorder of head (leaf), Otorrhea (leaf), Amenorrhea (root), Antifungal agents (root), Constipation (root), Dysmenorrhea (root), Leprosy (root), Paralysis (root), Stomatitis (root), Antifungal agents (stem), Abdomen (unspecified), Headache (unspecified), Anesthetic (unspecified), Astringent (unspecified), CNS depressant (unspecified), Emmenagogue (unspecified), Eye (unspecified), Hepatitis (unspecified), Lactogogue (unspecified), Mouth (unspecified), Narcotic (unspecified), Otorrhea (unspecified), Puerperium (unspecified), Ringworm (unspecified), Sedative (unspecified), Septicemia (unspecified), Skin (unspecified), Sore (unspecified), Tonic (unspecified), Tumor (unspecified), Vermifuge (unspecified), Vulnerary (unspecified), Whitlow (unspecified), Anodyne (unspecified), Pectoral (unspecified), Cirrhosis (unspecified), Corn (unspecified), Dysentery (unspecified), Perfume (unspecified), Anthelmintics (unspecified), Antifungal agents (unspecified), Antiparasitic agents (unspecified), Diuretics (unspecified), Emollients (unspecified), Menstruation-inducing agents (unspecified), Skin diseases (unspecified), Ulcer (unspecified), Burns (whole plant), Callosities (whole plant), Antineoplastic agents (whole plant excluding root), Diuretics (whole plant excluding root)
|