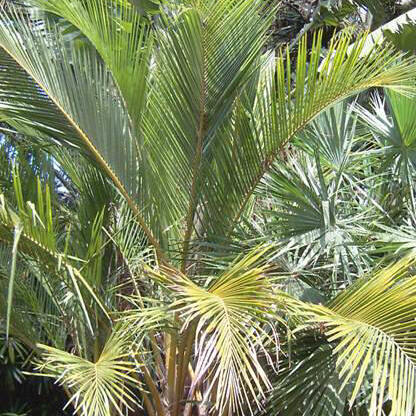
Clustered, pleonanthic, monoecious palm up to 8 m high. Stems up to 0.4 m in diameter, erect to reclining, branching at the base and also aerially by forking, bearing leaf sheath remains distally, eventually becoming bare, marked with close leaf scars. Leaves pinnate, up to approximately 6 m long, arranged in 5 vertical rows, marcescent or neatly abscising; sheaths tubular, soon disintegrating into an interwoven mass of fibres; rachis ± straight or curved; apparent petiole adaxially channelled, abaxially rounded; margins bearing leaf sheath fibre remains or becoming smooth; leaflets reduplicate, the tips mostly asymmetrically 2-lobed, abaxial surface bearing ramenta along the vein. Inflorescence solitary, interfoliar, branching to 1 order, shorter than the leaves; peduncle elongate, prophyll tubular, 2-keeled, enclosed within the leaf sheaths, splitting apically; peduncular bract tubular and entirely enclosing inflorescence in bud, later splitting longitudinally along abaxial face, becoming woody; rachis usually shorter than peduncle, bearing numerous spirally arranged, rather distant, spreading rachillae, each subtended by a low triangular bract; rachillae usually bearing proximally few to numerous spirally arranged triads consisting of 2 lateral staminate flowers and a central pistillate flower, distally bearing paired or solitary staminate flowers; rachilla bracts and floral bracteoles small. Staminate flowers sessile, 12-20 mm long; sepals 3, separate, imbricate, ± triangular, keeled; petals 3, separate, valvate, much larger than the sepals, boat-shaped with triangular tips, stamens (6)7-16, anthers basally sagittate, dorsifixed, introrse; pistillode small, irregularly trifid. Pistillate flowers ovoid, up to 10 mm long; sepals 3, separate, broad, rounded with pointed tips, imbricate; petals 3, separate, ± twice as long as sepals, broad, rounded, imbricate except at the short valvate triangular tips; staminodial ring collar-like, very briefly toothed or consisting of several irregular tooth-like lobes; gynoecium ovoid, trilocular, triovulate, stigmas 3, very short, ovules hemi-anatropous, laterally attached. Fruit 1-seeded, up to 40 mm long and 42 mm in diameter, orange at maturity, globose with a short apical beak, stigmatic remains apical; epicarp smooth, mesocarp thin, fibrous, endocarp thick and bony, with 3 vertical grooves, the pores lateral just below equator. Seed basally attached, endosperm homogeneous with a large central cavity; embryo lateral, next to one of the endocarp pores. Germination remote tubular, eophyll entire, lanceolate.
More
A palm up to 5-8 m tall. It always has several stems from the base. The trunks are short. The leaves are feather-shaped. They are 3-4 m long. They are stiff and dark green. There are no spines on the leaf stalk. There is a slight twist along the leaf stalk. Individual leaflets are stiff, very slender and with an unequal lobe at the tip. Male and female flowers are separate but on the same tree. The flowers are about 1 cm across. They occur in zigzag branched sprays. These occur amongst the leaves. The male flowers are on the upper part of the branches. The fruit are almost round and 3 cm long and 2 cm across. The milk and meat are eaten.
Perennial, multi-stemmed tree, up to 5(8) m high. Leaves pinnate or feather-shaped, 3-4 m long, apex obtuse, without spines. Flowers ± 10 mm in diam., in zigzag-branched sprays or panicles, monoecious. Male flowers: petals 3, free, much larger than sepals; stamens 8-16, shorter than petals. Female flowers: on lower branches, 2-or 3-locular with a single ovule in each locule. Fruit globose, with fibrous coating and hard endocarp.