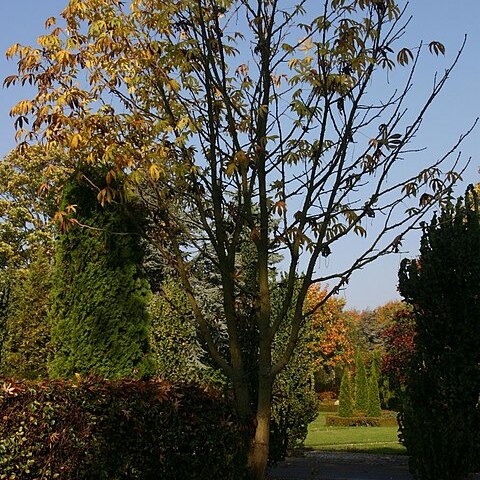
A tree up to 18-30 m high. It loses its leaves during the year. The crown is round. It has scattered stout prickles on the trunk. The leaves are large and lobed like fingers on a hand. There are 5-7 lobes. These are pointed and have fine teeth along the edge. The leaves are on long stalks. The leaves are dark green above and paler underneath. The flowers are small and white in round heads. The fruit are bluish-black berries. These are in clusters.