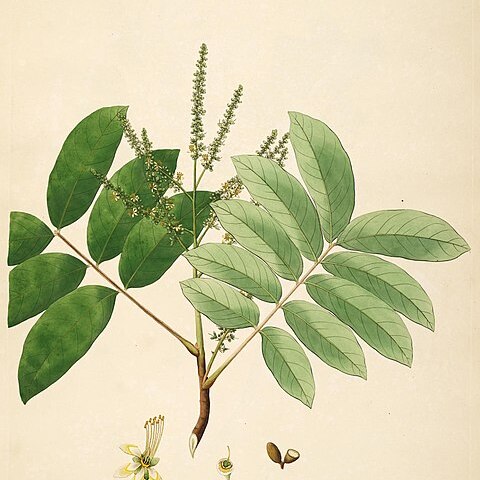
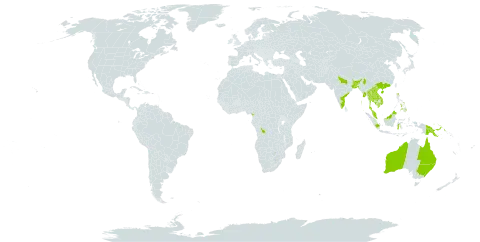
Shrub or small tree, up to 16 m high, dbh up to 28 cm (Forman 239 from N Celebes reported to be 30 m high with a diameter of 60 cm; from India also reported to be a fairly big tree). Indumentum ferrugineous to fulvous, sometimes and in some parts silvery-grey. Branchlets terete, grooved, c. 5(-15) mm in diam., densely short-hairy when young. Leaves (2-)3-6(-9)-jugate, often with a pseudo-terminal leaflet, velvety when young; petiole about terete, 7.5-12(-20) cm long, densely short-hairy, late glabrescent; petiolules up to 5(-10) mm long. Leaflets elliptic to lanceolate, (4.5-)6.5-18(-25) by (2-)3.5-8.5(-ll) cm, stiff chartaceous, above greyish green to grey, beneath yellowish green to reddish brown, on both sides shortly and densely hairy on midrib and nerves, sparsely so all over the surface mainly beneath (velvety on the touch), more or less glabrescent; base rounded to broadly cuneate; apex obtuse to acute or acuminate, often mucronulate; midrib prominent above, rather strong and rounded beneath, nerves 8—12(—16) on either side, ascending to spreading, nearly straight to slightly curved, bent at the margin, not distinctly joined but for few upper ones, hardly prominent above, slightly so beneath, veins and veinlets inconspicuous above, beneath densely reticulate-sca-lariform and prominulous. Inflorescences 25-35 (-50) cm long, densely ferrugineous tomentose; branches often long, ascending, spicate; cymes nearly sessile to short-stalked, glomerulous to distinctly branched, few to several-flowered; bracts and bracteoles small, subulate; pedicels l-2(-5) mm. Flowers sweet-scented. Sepals orbicular-ovate, slightly concave, green when fresh, margin sometimes petaloid, ciliate, inside glabrous or with a few hairs, outer two 1.2-2.2 by 1.2-2 mm, acute, inner three 1.8-2.8 by 2-3 mm, obtuse. Petals 4 (or 5), claw 0.5-1 mm, blade 2-4 by 1.5-2.2, crenu-late in upper half, white to yellowish when fresh, long ciliate in upper part of the claw and — sparsely — in the narrowed lower part of the blade, outside with a few hairs at the base; scale c. 1.5-3 mm long, quadrangular to ± bilobed, slightly narrowed from base to apex, bearded, the appendage deeply bilobed, the lobes sometimes also bilobed, hairy; the abaxial petals shorter and narrower than the adaxial ones, and with a shorter scale. Stamens longest abaxially; filaments flattened, long white hairy, in male flowers (1.5—)3—5 mm long, in female 1.5 mm; anthers oblong-ovate, 0.8 mm, glabrous. Ovary 3-lobed, 1.2-1.8 by 2-2.2 mm, densely appressed-hairy; style cylindric, 2.2 mm long, bent near the obscurely 3-lobed apex, sparsely appressed-hairy in the lower ⅔; pistilode in female flowers c. 0.8 mm high, long hairy. Fruits 1-, 2-, or 3-lobed, lobes spreading, 8-13 by 7-8 mm, faintly carinate, dark purple to nearly black when ripe, subglabrous; endocarp thin but hard and tough, glabrous. Seeds oblong-ellipsoid, 9-11 by 4 by 4 mm, hilum basal, small.
More
Shrubs or small trees, evergreen, usually 2-3 m tall, sometimes to 7 m tall. Bark dark brown, irregularly longitudinally fissured; young branches, inflorescences, and leaf axis densely ferruginous tomentose. Leaves with petiole 15-50 cm; leaflets 2-8 pairs; petiolules short, less than 5 mm, stout; blades abaxially becoming brown when dry, adaxially deep green, slightly shiny, first pair (near base) ovate, evidently smaller, gradually larger toward leaf apex, elliptic-ovate to narrowly elliptic, 3-20 cm, leathery, abaxially densely tomentose, adaxially hairy only on midvein and lateral veins, lateral veins ca. 10 pairs, tips not reaching margin, base broadly cuneate to rounded, margin entire, apex obtuse or rounded, rarely acute. Inflorescences compound racemose, only branched once, densely flowered on upper part of branches; bracts subulate. Flowers fragrant, ca. 5 mm in diam. Sepals suborbicular, 2-2.5 mm. Petals 4, obovate, ca. 5 mm. Filaments villous. Fertile schizocarps red, 1.2-1.4 cm × 5-7 mm. Fl. spring, fr. summer.
Tree to 10 m high. Leaf rachis 10–36 cm long; leaflets 4–10, elliptic-oblong or ovate-oblong, obtuse, subretuse or subacute, oblique and obtuse at base, 3–24 cm long, 3–6 cm wide, pubescent or puberulent; lateral veins 8–16 pairs; petiolules 2–5 mm long; petiole 5–14 cm long. Panicles 10–35 cm long; cymules 3–8-flowered; bracts subulate; pedicels 1–5 mm long. Sepals 5, usually suborbicular, 3–4 mm long, concave, silky outside except petaloid margin. Petals 5–6 mm long, subobovate, abruptly clawed, glabrous, white; scale 2-lobed, usually hooded, villous, crested; crests erect, linear. Stamens usually at opening of interrupted 3-lobed disc; filaments 3–5 mm long. Fruit 3-lobed, red or purple; lobes ellipsoidal, 8–15 mm long, puberulent or glabrous.
A shrub 1-3 m tall. It can grow to 10 m tall. It can spread 1-2 m wide. Trunks can occasionally be 35 cm across. The young branches are slightly grooved. They are covered with brown hairs. The leaves are 10-30 cm long and divided. There are 4-18 leaflets. These are 3-24 cm long by 3-6 cm wide. They are oval or oblong and largest towards the tip. They are dark green and leathery. There are brown hairs on both surfaces. The flower panicle is 10-35 cm long and it has many branches. The flowers are 0.6 cm across. They are white. The fruit is a capsule. The fruit are small and purple. They grow in clusters.