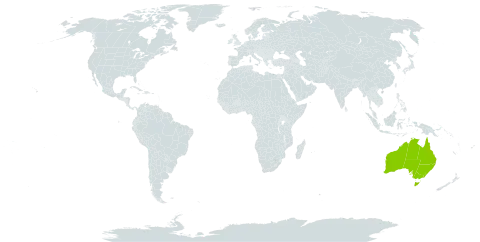
Herb, dioecious, rhizomatous, perennial, mostly forming tussocks 5–15 cm across. Rhizome stout, shortly creeping, 4–8 mm diam.; scales brown, covering a brown woolly pubescence. Culms spaced c. 1 cm apart, usually with a few erect branches below the inflorescence, 40–80 cm long, terete to subterete or compressed above a branching node, 0.5–2 mm diam., striate, pale-or yellow-green to brown, with closely appressed, pale, often caducous, scale-like trichomes. Sheaths 0.7–1.5 cm long, pale green to brown, glabrous or with pale, caducous, scale-like trichomes, acuminate with a short subulate tip to c. 3 mm long; margin membranous, 1–2 mm wide, caducous. Inflorescence: male spikelets semi-erect to pendulous, on lateral branches clustered at upper nodes; female spikelets in narrow, erect fascicles on peduncles that are sparsely tomentose with short white hairs. Male spikelets pedicellate, the pedicels filiform and to c. 1 cm long, the spikelets narrow-ovoid, 4–7 mm long; glumes up to c. 10, all fertile, ovate, aristate to mucronate, 2.5–3.5 mm long, chestnut to dark brown, glossy, glabrous, with hyaline membranous margin and a short awn 0.2–0.8 mm long. Female spikelets in dense clusters so that the spikelet structure is not prominent, narrow-ovoid and red-brown when flowering, becoming globose, spreading and grey-brown when fruiting; glumes ovate, aristate, 1–2 mm long with a short, erect awn, initially red-brown and rigid, becoming grey-brown and papery with age; floral bracts ovate, c. 1.5 mm long, glabrous. Male flowers: tepals 5 (lowest flower in spikelet with 6 tepals), lanceolate, acute, 1.6–2.3 mm long, membranous; 2 outer tepals keeled; inner tepals flatter, slightly shorter; stamens 3, filaments 0.1–0.4 mm long, anthers 0.6–1.0 mm long. Female flowers: tepals 6, ovate, acute, 1–1.5 mm long, brown-hyaline, initially glabrous but becoming densely pubescent adaxially with age; outer tepals keeled; inner tepals flat, more densely fimbriate; style 3-branched, connate at the base, filiform, the upper half stigmatic. Nut trigonous, 0.8–1.0 mm long, glossy brown. Seed c. 0.8 mm long. Culm anatomy: chlorenchyma interrupted by groups of pillar cells that extend from the parenchyma sheath to the epidermis.