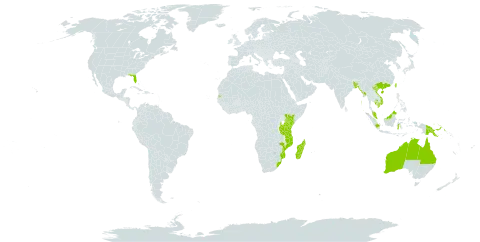
Small tree or shrub up to 9 m. high; bark rough, reddish brown; young branchlets reddish or grey, sometimes appressed pubescent at first, soon glabrescent.. Leaves spirally arranged; lamina narrowly obovate or narrowly obovate-elliptic to elliptic, 2–8 cm. long, 1–3 cm. wide, apex rounded, cuneate to the subsessile base or sometimes narrowed to appear subpetiolate.. Inflorescences usually single, sometimes branched, axillary spikes 2–7 cm. long; rhachis glabrous.. Flowers sessile or nearly so.. Receptacle tubular or narrowly urceolate, laterally compressed, 6–8 mm. long, glabrousor pubescent, usually contracted just above the middle at the insertion of the 2 opposite or subopposite adnate bracteoles; bracteoles broadly ovate, 1.5 mm. long, sometimes ciliolate.. Sepals broadly ovate-acuminate, 0.8–1 mm. long, sometimes gland-tipped.. Petals white or cream (? sometimes pink) or yellow (var. lutea (Gaud.) Exell, confined to Timor), narrowly elliptic or narrowly obovate-elliptic, 4 mm. long, 1 mm. wide, glabrous.. Stamens 10, equalling or slightly exceeding the petals.. Style 6–7 mm. long, glabrous.. Fruit 10–12 mm. long, 3–5 mm. wide, appressed pubescent or glabrous; pericarp with a well-developed inner layer of sclerenchyma.. Fig. 13.
Small tree up to 9 m high or shrub; bark rough, reddish-brown; young branchlets reddish or grey, sometimes appressed-pubescent at first, soon glabrescent. Leaf-lamina 2-9 x 1-3 cm, narrowly obovate or narrowly obovate-elliptic or narrowly elliptic, cuneate to the subsessile base or sometimes narrowed to appear subpetiolate. Inflorescences of short axillary spikes 2-7 cm long; rhachis glabrous. Flowers sessile or nearly so. Receptacle 6-8 mm long, tubular or narrowly urceolate, laterally compressed, glabrous or pubescent, usually contracted just above the middle at the insertion of the 2 broadly ovate 1.5 mm long sometimes ciliolate opposite or subopposite adnate bracteoles. Sepals 0.8-1 mm long, broadly ovate-acuminate, gland-tipped or eglandular. Petals white or cream (? sometimes pink) or yellow (var. lutea), 4 x 1 mm, narrowly elliptic or narrowly obovate-elliptic, glabrous. Stamens 10, equalling or slightly exceeding the petals. Style 6-7 mm long, glabrous. Fruit 10-12 x 3-5 mm, appressed-pubescent or glabrous; pericarp with a well-developed inner layer of sclerenchyma with a spoke-like appearance in cross-section.
Shrubs or small trees, to 8 m tall; trunk to 0.3 m d.b.h. Bark brown or grayish black, coarse. Branchlets red or grayish black. Leaf blade pale green adaxially, spatulate to oblanceolate or obovate, 3.5-7 × 1-2.5 cm, apex retuse or rounded; lateral veins usually in 3 or 4 pairs. Inflorescences axillary, 2-6 cm. Flowers fragrant. Calyx tube ca. 9 mm; bracteoles ca. 1 mm; lobes deltoid, 1-2 mm, apex obtuse or shortly mucronate. Petals white, elliptic, 4.5-5 mm, apex obtuse. Stamens 5 or 10, 4-5 mm, shorter than or equaling petals. Style ca. 4 mm. Fruit blackish brown when ripe, ellipsoid or ovoid, slightly compressed on one side, 1-2 cm × 5-8 mm excluding stipe, 2-or 3-ridged, smooth proximally, longitudinally striate distally; stipe ca. 1 mm. Fl. Nov-Aug, fr. Aug-Apr.
A shrub or small tree. It grows to 4-8 m tall and spreads to 1-2 m wide Young plant parts have small hairs. The bark is rough and dark grey and has slight cracks along it. The leaves are often clustered near the ends of branches. They are arranged in spirals. The leaves are oval and 3-6 cm long by 1-2 cm wide. They are rounded at the tip and taper at the base. They are leathery and light green. There is often a notch at the tip of the leaf. The flowering stalks in the axils of leaves are branched and produce 3-7 flowers. The flowers are fleshy and white. The flower lobes are triangular and petals are 4 mm long by 1 mm wide. The fruit is narrow and oval. It is 12 mm long by 4 mm wide. The fruit is fibrous and has a single seed.
Shrub or small tree to 8 (–10) m high, without pneumatophores. Branchlets appressed pubescent, glabrescent. Leaves: lamina obovate, 2–9.5 cm long, 1–2.5 cm wide, cuneate at base, entire, sometimes appearing crenate due to presence of glands, retuse at apex, often with minute hairs at first, glabrescent; petiole absent or to 10 mm long. Inflorescence a short axillary spike. Flowers sessile, white. Ovary ± cylindrical, 6–8 mm long, expanded above in a calyx tube with broadly ovate, acuminate lobes c. 1 mm long. Petals to 4 mm long, c. 1 mm wide. Stamens usually 10, about as long as petals. Style to 7 mm long. Fruit narrowly ovoid, 1–1.5 cm long including persistent calyx lobes.
Small tree up to 9 m. high or shrub; bark rough, reddish-brown; young branchlets reddish or grey, sometimes appressed-pubescent at first, soon 2, flower (x6); 3, longitudinal section of flower (x6), 2–3 from Vaughan 461; 4, young fruit (x4); 5, transverse section of fruit (x6), 4–5 from glabrescent.
Receptacle 6–8 mm. long, tubular or narrowly urceolate, laterally compressed, glabrous or pubescent, usually contracted just above the middle at the insertion of the 2 broadly ovate 1·5 mm. long sometimes ciliolate opposite or subopposite adnate bracteoles.
Leaf-lamina 2–9 x 1–3 cm., narrowly obovate or narrowly obovate-elliptic or narrowly elliptic, cuneate to the subsessile base or sometimes narrowed to appear subpetiolate.
Fruit 10–12 x 3–5 mm., appressed-pubescent or glabrous; pericarp with a well-developed inner layer of sclerenchyma with a spoke-like appearance in cross-section.
Petals white or cream (? sometimes pink) or yellow (var. luted), 4 x 1 mm., narrowly elliptic or narrowly obovate-elliptic, glabrous.
Sepals 0·8–1 mm. long, broadly ovate-acuminate, gland-tipped or eglandular.
Inflorescences of short axillary spikes 2–7 cm. long; rhachis glabrous.
Stamens 10, equalling or slightly exceeding the petals.
Flowers sessile or nearly so.
Style 6–7 mm. long, glabrous.