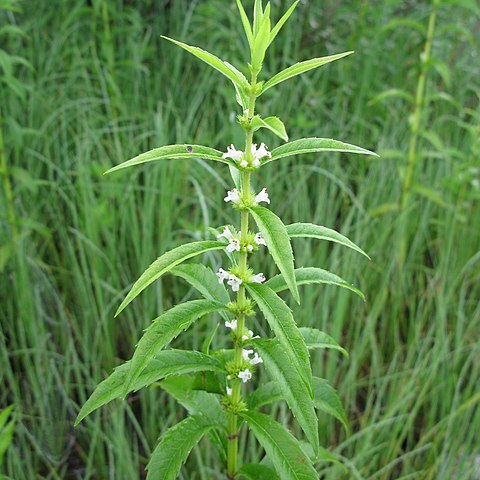
Herbs perennial. Rhizomes swollen at apex, sometimes with enlarged stolons bearing scalelike leaves. Stems erect, 20-70 cm, usually unbranched, nodes ± tinged purple-red. Leaves subsessile or short petiolate, linear to oblong-lanceolate, ± arcuate, 4-8 × 1.2-2.5 cm, glabrous to minutely hispid-hirsute, abaxially impressed glandular, base attenuate, margin ± pinnatipartite to ± entire, apex acuminate. Verticillasters globose, 1.2-1.5 cm in diam.; bracteoles ovate to lanceolate, ciliolate, spinescent, outermost to 5 mm and 3-veined, inner ones 2-3 mm and 1-veined. Calyx ca. 3 mm, glabrous, glandular; teeth 5, lanceolate-triangular, ca. 2 mm, apex spinescent, ciliolate. Corolla white, ca. 5 mm, glandular, throat white pubescent, tube ca. 3 mm; limb indistinctly 2-lipped, upper lip subcircular; lower lip 3-lobed, middle lobe larger. Nutlets obovoid, 4-sided, ca. 1.6 × 1.2 mm, abaxially flattened, glandular, base subattenuate. Fl. Jun-Sep, fr. Aug-Nov.
More
A herb. It keeps growing from year to year. The rhizomes or underground stems are swollen at the tip sometimes with enlarged stolons bearing scale like leaves. The stems are erect. They are 20-70 cm high. The nodes are tinged purple-red. The leaves have very short leaf stalks. The leaf blades are 4-8 cm long by 1.2-2.5 cm wide. The flower heads are round and 1.2-1.5 cm across. The flowers are white.