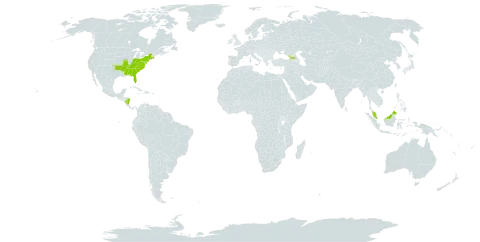
Small tree to 10 m; winter terminal bud 2–3 cm, glabrous; lf scars with minute resin glands; lvs closely clustered beneath the fls, deciduous, thin, lance-obovate, at anthesis 1.5–2 dm, at maturity to 5 dm, abruptly and sharply acuminate, tapering from the middle to an acute base, the lower surface green, finely and sparsely hairy; fls white, malodorous; pet 6–9, oblanceolate to narrowly obovate, spreading, 8–14 cm; style thick, persisting as a beak on the glabrous follicle; fr-cone ellipsoid-cylindric, 7–12 cm; 2n=38. Rich woods; Ga. to Ark., n. to s. Pa., W.Va., O., Ky., and e. Mo. May.