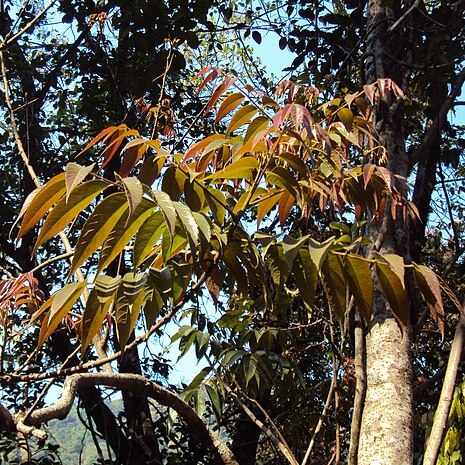
Trees to 15 m tall, evergreen or deciduous. Leaves odd pinnate; leaflets 11-25, lanceolate on lower axis, lanceolate or narrowly oblong on mid-axils, terminal one suboblanceolate, 7-17 × 2-4 cm, papery or subleathery, both surfaces nearly glabrous, lateral veins 10-14 pairs, somewhat ascending, arched-anastomosing 2-5 mm from margin, base cuneate or broadly cuneate, margin sparsely serrate or nearly entire, apex caudate-acuminate. Panicle erect, 10-55(-70) cm, pubescent, axis long and stiff, triangular, broadly and sparsely branched. Sepals 5, broadly ovate, 6-8 mm, 2 outer ones narrower. Petals: 3 outer ones suborbicular; 2 inner ones bifid to half. Ovary glabrous. Drupe globose or obovoid, 4-5 mm in diam.; endocarp globose, convex, with coarse, scattered netlike strips, midrib prominent. Fl. May-Jun, fr. Sep-Oct.
A tree. It grows 1 to 42 m high. The trunk is 75 cm across. The leaves can be 60 cm long. This includes a leaf stalk 15-25 cm long. There are 3-7 pairs of leaflets. They are oblong to sword shaped. They are usually larger towards the tip. They are 20 cm long by 6 cm wide. There are 3-15 pairs of secondary veins. The flowering cluster is at the end of the branch. These are erect and 10-70 cm long. The fruit is round and hairy. It is 3-11 mm across. It is red.