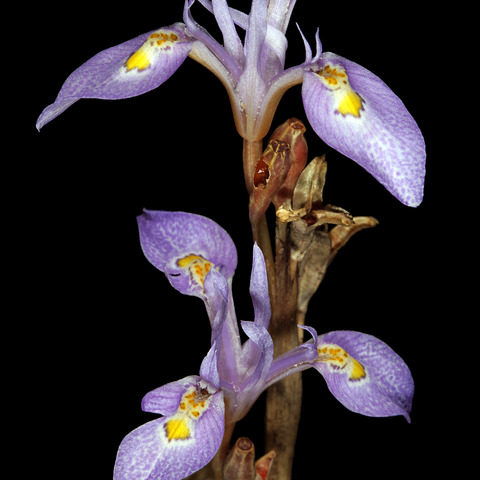
Plants usually 15-25 cm. high.. Corm 1-3 cm. diameter, tunics of medium to coarse dark brown fibres, often bearing cormlets among the fibres.. Foliage leaf solitary, usually absent at flowering time (or dead and still attached to base of stem), rarely the new leaf emerging, eventually produced to ± 60 cm. or more, terete, without an adaxial groove, ± 1.5 mm. diameter.. Stem erect, usually bearing 3-6 branches, these held close to the main stem, sessile or on short branches concealed by the subtending sheathing leaves, these dry and brownish, 3-6 cm. long, apices often lacerated.. Rhipidia with spathes dry and papery, rarely green near the base, the inner (2.5-)3-4 cm. long, apices membranous, speckled darker brown, sometimes lacerated, the outer usually ± 2/3 as long as the inner.. Flowers pale lilac to blue-violet with yellow-orange spotted nectar guides on the outer tepals.. Outer tepals 1.9-2.4 cm. long, claw ascending, narrow, slightly shorter than the limb, limb ovate-lanceolate, ± 1.1-1.4 mm. long, 5-8 mm. wide, reflexed; inner tepals linear-lanceolate, erect or ascending, 15-18 × 2-4 mm.. Filaments 3-4 mm. long, united in the lower third; anthers 5-6 mm. long.. Ovary 5-6 mm. long, the style-branches 7-8 mm. long, crests 3-6 mm. long.. Capsules obovoid, 8-11 mm.. Fig. 2/4.
Perennial herb, geophyte, 0.15-0.25 m high; corm with dark brown tunics of medium to coarse fibres; stem erect, usually with 3-6 branches held close to main stem. Leaf 1, usually absent at flowering time, terete. Spathes dry, papery, rarely green near base, lacerated. Inflorescence with pale lilac to blue-violet flowers; nectar guides spotted yellow-orange; tepals lanceolate, outer 19-24 mm long, reflexed, claw ascending, inner 15-18 mm long, erect or ascending. Stamens: filaments 3-4 mm long, united in lower 1/3; anthers 5-6 mm long; pollen orange. Ovary nearly cylindric, 5-6 mm long; style branches 7-8 mm long, diverging; crests narrow. Flowering time Sept.-Nov. Capsule obovoid.
Flowers pale-lilac to blue-violet with yellow-orange spotted nectar guides on the outer tepals; tepals unequal, the outer 19–24 mm long with an ascending claw narrow and slightly shorter than the limb, limb c. 11–14 × 5–8 mm, obovate to lanceolate, reflexed; the inner tepals 15–18 × 2–4 mm, linear-lanceolate, erect or ascending.
Cormous geophyte, up to 250 mm high. Leaf solitary, absent at flowering; blade linear, up to 0.6 m long. Flowers: flowering stem erect with 3-6 short branches; style crests > 2 mm long and acute; perianth with segments > 20 x 1.5 mm, pale lilac to blue-violet with yellow-orange spotted nectar guides on outer segments; Jul.-Oct.
Foliage leaf solitary, usually absent or beginning to emerge at flowering rime (dead leaf from previous season sometimes still attached to base of stem), eventually up to c. 60 cm long or more, c. 1.5 mm in diameter, terete, without an adaxial groove; sheathing leaves dry and brownish, 3–6 cm long, often apically lacerate.
Rhipidia sessile or on short branches concealed by the subtending sheathing leaves; spathes dry and papery, rarely green near the base, the inner (2.5)3–4 cm long with apices membranous speckled darker brown and sometimes lacerated, the outer usually about two-thirds as long as the inner.
Cormous herb, up to 250 mm tall. Plant leafless when in bloom. Style crests present, at least 2 mm long and acute. Inner tepals longer than 10 mm. Lateral branches short to sessile. Flowers pale lilac to blue-violet with yellow-orange spotted nectar guides on outer tepals.
A herb. It keeps growing from year to year. It grows 15-25 cm high. The corms are 1-3 cm across. There is a single leaf. It is 1.5 mm wide and 60 cm long. The stem is branched with branches close to the stem. The flowers are pale lilac or blue with orange-yellow spots.
Corms 1–3 cm in diameter; tunics of medium to coarse, dark-brown fibres, cormlets often present amongst the fibres.
Style branches 7–8 mm long, diverging about 1.5 mm above the base; style crests narrow, 3–6 mm long.
Filaments 3–4 mm long, united in the lower third only, anthers 5–6 mm long.
Stem erect, usually 3–6-branched; branches held close to the main stem.
Capsules 8–11 mm long, obovoid.
Plants usually 15–25 cm high.