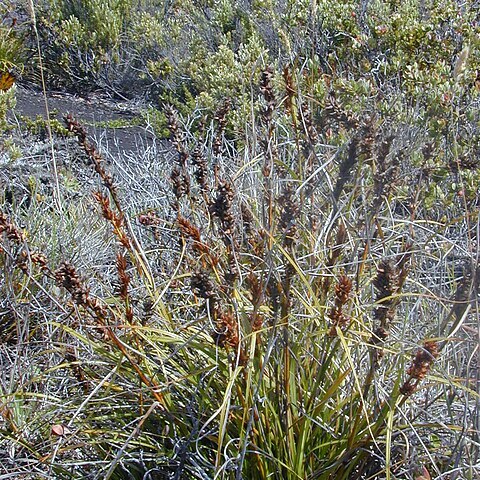
Perennial tufted herbs, 0.7–1.2 m high; plants clonal, 0.2–0.8 m across; rhizome thick, 5–15 mm diam., woody, short, branched, pseudobulbous or not; old leaf sheaths covering the rhizome, breaking apart into fibres with age or not, dark brown to blackish brown; roots sand-binding or not. Culms stout, erect, with 0, 1, 3 or 4 leafy nodes, trigonous or ± terete, 1.0–5.5 mm diam., multi-striate, glabrous or rugulose. Caudex absent. Leaves mostly basal, numerous, and with 0, 1, 3 or 4 cauline; phyllotaxy loosely spirotristichous, sheath glabrous or sometimes pubescent (then glabrescent), tight around culm, 8–60 mm long, 1.2–6 mm wide, ± equal in width to or broader than the leaf lamina, pale brown to dark brown to blackish brown, upper margin usually with fine, blunt scabrous projections, ligule absent; pseudopetiole present or not obvious; basal leaves 12–62 cm long, 2–8 mm wide, lamina ± linear, sometimes twisted or curved, finely multi-striate, glabrous or midrib scabrous, dark green, often slightly paler below, margins usually finely bluntly scabrous, sometimes revolute or involute, apex long-attenuate. Inflorescence open or dense, panicle-like, narrow, linear to lanceolate, 5–35 cm long, 5–35 mm wide, axis green, not glaucous; with 3–8 nodes; bracts leaf-like, becoming progressively smaller up the culm, ± equal to greatly exceeding the spikelet clusters, basal bract shorter than to exceeding inflorescence; branches erect, basal branch 2–7 cm long, with 2–20 clustered spikelets on peduncles 0.5–5 mm long, arising in each bract axil; spikelet prophyll present, sheath 1.2–4.5 mm long, brown, with 3 distinct veins, partially enclosing the spikelet, with a slender lamina 0.2–8.5 mm long, brown to green. Spikelets chestnut to brown, lanceolate to ovate, 6.5–15 mm long, not compressed, with 5–8, rarely 9, glumes, usually 1 or 2 fertile florets, sometimes 3, upper glume with a sterile male flower, second upper glume bisexual fertile, lower glumes empty, or rarely the third upper glume with a bisexual sterile or male-fertile flower, glumes spirodistichous, basal glume 2.5–7.8 mm long, fertile glumes 4.5–11.5 mm long, 1.6–3.5 mm wide, glabrous, scabrous or pubescent, especially on keel and towards the apex, elliptic-lanceolate, acute to acuminate, weakly keeled, with a mucro 0.4–3.0 mm long; rachilla mostly compact, but shortly sinuous around nutlet in fruiting spikelets in some species. Perianth segments absent or sometimes 2 or 6 segments present, 0.4–1.6 mm long, filiform, glabrous. Stamens usually 3, 6 or 8, rarely 4 or 9; anther connective 4.3–9.6 mm long, linear; anthers yellow or pale yellow, linear-oblong, 3.1–6.5 mm long, base auriculate, apex with a glabrous or scaberulous appendage 0.5–2.0 mm long. Style usually 3-branched (but 3–5 in M. octandra), base 3–7.3 mm long, glabrous or finely scabrous, thin above, thin or dilated below, branches 2.5–10 mm long. Nutlet straw-coloured, pale brown, brown or black, sessile (or shortly stipitate in M. microcarpa), angular globose, strongly 3 (–5)-ribbed, 2.1–5.4 mm long including the style base, 0.8–2.3 mm diam., epidermal cells square, oblong, semi-circular or hexagonal, but inconspicuous; apex sometimes with a very distinct persistent style base, depressed-ovoid, pyramidal or shortly conical, somewhat constricted at the base, scabrous-pubescent, 0.5–2.0 mm long; embryo Schoenus-type. Photosynthetic pathway inferred from anatomy to be C3.
More
Infl. an erect narrow panicle. Spikelets 2-fld, only lower fl. setting fr.; uppermost internode of rhachilla elongated and curved. Glumes clearly distichous, lower ones caducous. Hypog. bristles 0. Stamens 3. Style-branches 3. Fr. held by the persistent stamens and clasped by the inrolled margins of the persistent upper glumes; persistent style-base not readily distinguishable externally. Culms trigonous. Lvs spirally arranged, dorsiventral, margins harshly scabrid, revolute when dry. Two spp.: the type M. gahniaeformis Gaud. from Hawaii; the N.Z. sp. endemic.