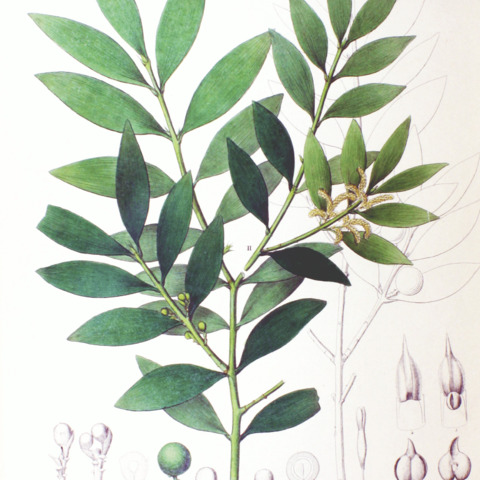
Trees evergreen, dioecious or rarely monoecious; crown columnar. Leaves spirally arranged or in decussate, opposite pairs on leading shoots, opposite or subopposite on lateral shoots, ± monomorphic, adult leaves similar to juvenile leaves but often larger or wider (although juvenile leaves larger in Nageia wallichiana), more than 5 mm; petiole twisted through 90° ; blade broadly ovate-elliptic to oblong-lanceolate, without obvious midvein but with many, slender, parallel, longitudinal veins converging toward base and apex, stomatal lines abaxial or rarely on all surfaces. Pollen cones axillary, solitary or clustered in small, spikelike groups of 3-6, borne on naked peduncles, ovoid-cylindric, with basal sterile scales; pollen 2-saccate. Seed-bearing structures terminal on short, scaly, axillary branchlets, solitary or occasionally paired; bracts usually obsolete, scarcely thicker than peduncle, rarely succulent and thicker than peduncle; ovule inverted. Epimatium wholly enveloping seed, leathery, with bluish black bloom when ripe. Seed drupelike, globose.
Dioecious, erect shrubs or trees, 1-54 m tall. Bark tan to brown within and dark brown to black on the surface but often weathering to gray, peeling in irregular shaped plates to short vertical strips. Leaves opposite-decussate (or mixed with some leaves spirally placed), distinctly narrowed to a decurrent base Juvenile leaves mostly larger than the adult leaves which are otherwise similar twisted at the base so as to appear distichous, in most cases amphistomatic with the abaxial face uppermost on the left side of the shoot and the axial face uppermost on the right side (in a few species the leaves are hypostomatic and without this unique orientation). Pollen cones sessile or terminal, solitary or grouped, cylindrical (or oval). Each inverted seed completely covered by the fertile scale (epimatium), one or occasionally two subterminal on a scaly shoot, the usually persistent leathery covering becoming more or less fleshy when ripe.
Erect shrubs or trees, 2-43 m high. Foliage buds a loose cluster of rounded scales; at the apex of foliage shoots not destined to continue growth there are found only a few very reduced leaves. Leaves with a single vascular bundle, lanceolate, oval to nearly linear, acute or rounded at the apex, less than 5 times as long as wide, amphistomatic, distichous when juvenile and adult (adult leaves sometimes not distichous), sessile or with a very short petiole. A part of the not fleshy fertile shoot remaining attached to the seed and its covering when it falls. Seed ovate or globular with an elongated beak at the micropylar end.