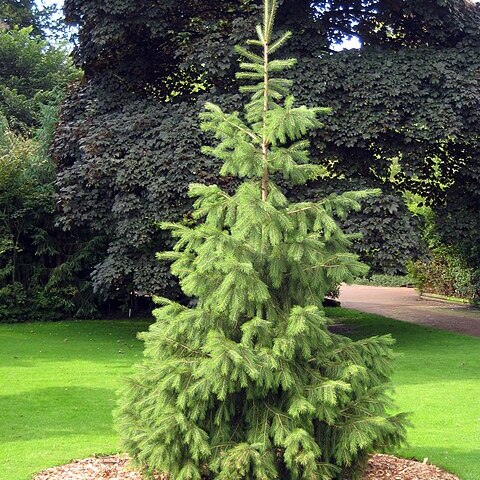
Trees to 60 m tall; trunk to 2 m d.b.h.; bark pale brown, breaking into irregular plates; crown conical; branchlets pendulous, pale brown or pale gray when young, glabrous; winter buds reddish brown, conical or ovoid, scales slightly open, rarely appressed at base of branchlets. Leaves spreading radially, directed obliquely forward, quadrangular-linear, slender, curved, quadrangular or subquadrangular in cross section, 3.3-5.5 cm × 1.3-1.8 mm, stomatal lines 2-5 along each surface, apex acute or acuminate. Seed cones green, maturing brown, lustrous, cylindric or fusiform-cylindric, 10-18 × 4.5-5 cm. Seed scales broadly obovate, thick, ca. 3 × 2.4 cm, rigid, base cuneate, apex entire, broadly triangular-obtuse. Seeds dark brown, ca. 5 mm; wing ovoid-oblong, 1-1.5 cm, apex pointed.
More
A large tree. It can be 60 m tall. The trunk is 2 m across. The bark is pale brown and breaks into irregular plates. The plant has a weeping habit with the branches hanging downwards. The leaves are spreading. The leaves are 3.3-5.5 cm long by 1.3-1.8 mm wide and dark green. The cones are green and 10-18 cm long by 4.5-5 cm wide. They are pointed at both ends. As they mature they turn purple. The seeds are dark brown and about 5 mm wide.
It is a temperate plant. It is frost hardy, once established. They grow in alpine soils between 2300-3600 m altitude in China. It suits hardiness zones 6-8. Arboretum Tasmania. Kyneton Botanical Gardens.
More
Usually found on N. and W. slopes inhabiting the drier upper areas often in association with silver fir or deodar; at elevations from 2,100-3,600 metres.