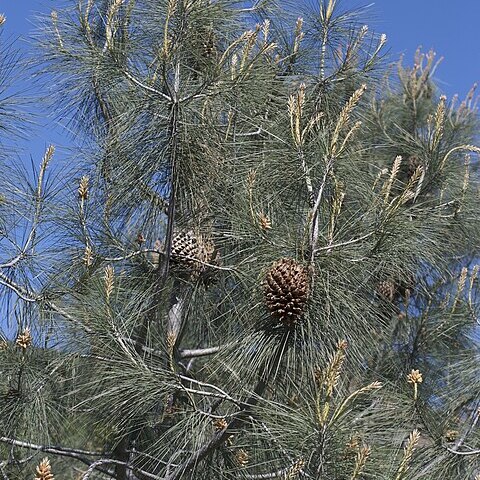
A medium sized tree. It grows 21 m high and spreads 6 m wide. The crown is irregular in shape. The trunk is often forked. The trunk is often free of branches for considerable height. The leaves are grey-green and are drooping. They can be 17-32 cm long. The cones are large up to 15-25 cm long. They can remain on the tree for 7 years after the nuts have fallen. The cones have heavy spikes. The seeds are edible. The seeds are 2 cm long.