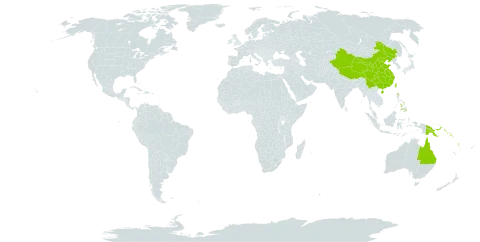
Dioecious vine. Leaves with petioles 0.4–3 cm long; lamina ovate to narrowly ovate-elliptic, 5–16 cm long, 2.2–8.5 cm wide, glabrous or with a few short hairs at base and on petiole; base cuneate or lobed, commonly asymmetric; apex acuminate; 1 or 2 pairs of secondary veins radiating from base of midvein, another pair slightly above. Spikes solitary, leaf-opposed, pendulous, 2–4 mm wide; peduncle 0.8–1.8 cm long; bracts adnate to rachis, broadened apically, margins free. Rachis hairy: male 5.2–11.5 cm long; female 7–19 cm long. Stamens 3. Stigmas 3, sessile. Fruiting spike 7–19 cm long, 2–4 mm diam. Fruit sub-sessile to sessile, ovoid to spherical, free, arranged at intervals along rachis, green to black.
A slender vine. The stem is 2 cm across. The leaves are 8-12 cm long by 4-7 cm wide. The leaf stalk is 1-1.5 cm long. The flowers are opposite the leaves. The flowering shoots are 7-9 cm long.