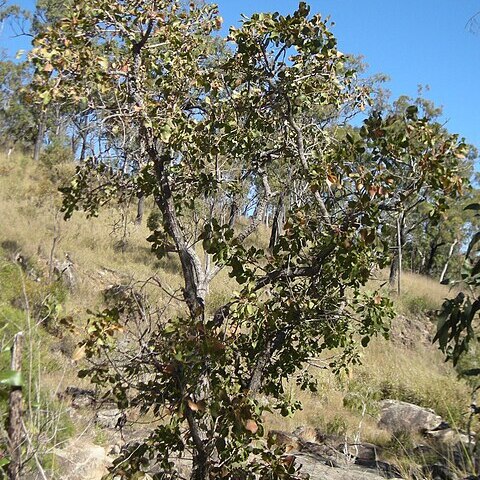
Trees or rarely shrubs. Leaves simple, spirally arranged, crowded at the end of the branchlets, penninerved, glabrous, membranaceous to coriaceous, base slightly decurrent or decurrent petioles narrowly winged, margin crenulate to denticulate or sub-entire to entire, without pellucid dots, caducous. Inflorescences terminal, racemes, spikes or sometimes flowers solitary. Flowers 5-merous, tribracteate, bracts and bracteoles subpersistent; bracteoles opposite. Sepals 4, connate at the base into a turbinate or campanulate tube with a gibbose margin in between the lobes; lobes imbricate. Petals 4, free, veined, attached at the base to the staminal tube, imbricate. Stamens numerous, multiseriate, unequal, contortoduplicate, in whorls, the inner whorl sterile, shorter than the outer whorl, the basal part connate into a tube; filaments filiform, longer than the petals; anthers small, 2-celled, basifixed, ovate-oblong to oblong, base and apex emarginate, longitudinally dehiscent; staminal tube and corolla caducous as a whole. Disc intrastaminal, epigynous, consisting of a vortex of the ovary and a rim. Ovary turbinate, adnate to the calyx tube, inferior, 3-4-locular; ovules horizontal, numerous, on whole length of central part of carpel, biseriate (irregular in P. grandis), campylotropous, funicle long, suspended; locule empty at the base; style slender, longer than the stamens; stigma small, cruciately capitate to capitate, lobed. Fruits fibrous, without pulp, indehiscent, obovoid to ovoid to ellipsoid or globular, 1-4-locular, crowned by the persistent calyx; pericarp fibrous; endocarp coriaceous. Seeds one to many in each locule, ovoid, smooth or angular, without endosperm; radicle very long, clavate, spirally convolute around the cotyledons or curved (in P. careya); cotyledons small, foliaceous, plicate (straight and attached to the radicle in P. careya).
More
Trees. Leaves crenulate or entire. Flowers in short racemes or solitary, terminal, conspicuous; bracts oblong, sub-persistent; receptacle shortly obovoid. Calyx-lobes 4, scarcely connate at base, imbricate. Petals 4, spreading. Stamens many, multi-seriate, shortly united, the outermost or innermost, or both, sterile; corolla and staminal tube deciduous together. Ovary inferior, 3 or 4-locular; ovules several per locule, biseriate along axis; style filiform, exceeding stamens; stigma small, simple. Fruit a globular to ellipsoidal berry, crowned by persistent calyx-lobes. Seeds several, in Australian species embedded in fleshy pulp; embryo spirally curved.