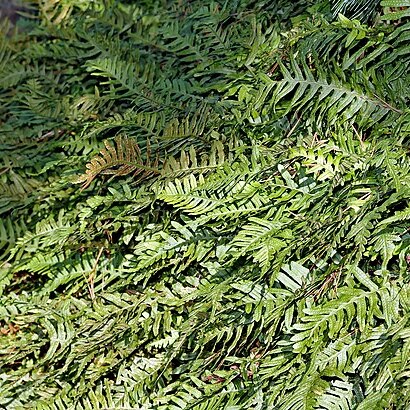
Plants mostly epiphytic and epilithic, a few terrestrial. Rhizomes shortly to long creeping, dictyostelic, bearing scales. Fronds monomorphic or dimorphic, mostly simple to pinnatifid or 1-pinnate (uncommonly more divided); stipes cleanly abscising near their bases or not (most grammitids), leaving short phyllopodia; veins often anastomosing or reticulate, sometimes with included veinlets, or veins free (most grammitids); indument various, of scales, hairs, or glands. Sori abaxial (rarely marginal), orbicular to oblong or elliptic, occasionally elongate, or sporangia acrostichoid, sometimes deeply embedded, sori exindusiate, sometimes covered by caducous scales (soral paraphyses) when young; sporangia with 1-3-rowed, usually long stalks, frequently with paraphyses on sporangia or on receptacle; spores hyaline to yellowish, reniform, and monolete (non-grammitids), or greenish and globose-tetrahedral, trilete (most grammitids); perine various, usually thin, not strongly winged or cristate. Mostly x = 35, 36, 37.
Epiphytic, lithophytic or rarely terrestrial ferns. Rhizome usually creeping, covered with peltate or pseudopeltate scales. Fronds monomorphic to strongly dimorphic, borne in 2 rows on the upper side of the rhizome and mostly articulated to it; lamina simple, lobed, pinnate or dichotomously branched; humus-collecting fronds present in some genera. Veins nearly always reticulate; areoles usually with free included veinlets. Sori exindusiate, sometimes protected when young by umbrella-shaped or stellate paraphyses, either round and sometimes sunken in cavities in frond surface, or elongated and parallel to main veins (and therefore oblique to midrib) or to margin, or covering all or a specialised part of the frond. Spores 64 per sporangium, rarely (not in Australia) 8 or 16, bilateral, mostly smooth or tuberculate, monolete (very rarely globose and trilete), often translucent and colourless or yellow (very rarely chlorophyllous), with or without a prominent, variously-shaped perispore.
Terrestrial, epiphytic or less often on rocks. Rhizomes short to long and creeping with basifixed pseudopeltate or peltate clathrate opaque or hyaline entire toothed or ciliate scales
Epiphytes, rarely terrestrial, with creeping rhizomes containing a ring of small vascular bundles; scales peltate, clathrate or not