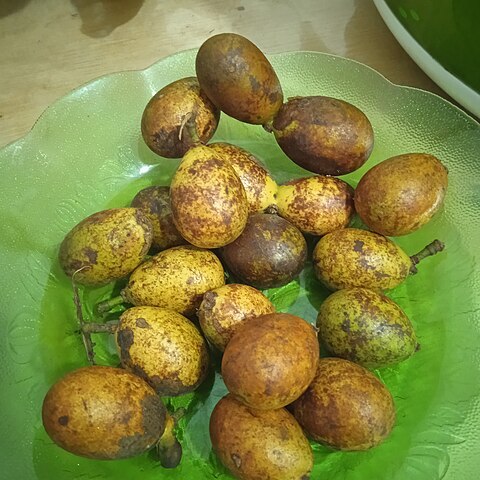An evergreen tree. It can grow into quite a large tree up to 40-50 metres high. At the base of the tree there are often large buttresses and the bark is a bright orange brown colour and rough and scaly. The hard timber is widely used. The young leaves and twigs of the tree are bright red. The lowest pair of leaflets are small and clasp the stem like stipules. There are often 5-11 pairs of leaflets along a stalk and the leaflets at the centre are often the largest. The leaflets droop from long stalks. The flowers are produced in clusters on stalks that are up to 50 cm long and grow near the ends of the branches. The flowers are small and yellowish green and do not have any scent. The skin of the ripe fruit peels off like a mandarin. The edible part is a clear layer around the seed, like in a rambutan. An inedible kind also occurs. The fruit is about 6 cm across and the seed about 3 cm across.
Trees, large, ca. 20 m tall, to 50 m tall. Crown large, broad, with evident buttress roots; branches grooved, sometimes hirsute. Leaves rather large, with petiole to 1.5 m, axis and leaflets subglabrous to tomentose; leaflets dense, 5-9 pairs, sometimes to 15 pairs, subopposite; petiolules short, inflated; blades: first pair orbicular, small, base cordate, stipulelike; others oblong or upper ones nearly cuneate, 15-40 × 5-10 cm, margin regularly serrate, apex acute or acuminate. Inflorescences terminal or axillary; rachis and branches strong, straight, 30-50 cm, pilosulose. Pedicels ca. 6 mm, base jointed. Sepals ca. 1 mm, pilosulose. Petals obovate-triangular, ca. 2 × 2 mm. Stamens ca. 5 mm. Fruit shiny, ellipsoid or sometimes subglobose, ca. 3 × 2 cm, glabrous.
A large tree with a crooked irregular stem. The leaves are large and alternate. They have 4 to 9 pairs of leaflets. The flower arrangement is at the ends of branches and is profuse. The flowers are small and yellowish white. The fruit is round 3 cm across and hard and brittle. The skin of the ripe fruit peels off like a mandarin. The edible part is a clear layer around the seed, like in a rambutan.