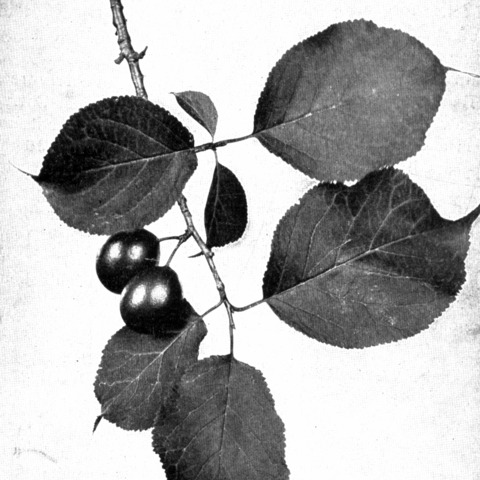
A very small tree. It grows up to 9 m tall. The trunk can be 25 cm across. The trunk is short and crooked and often divided into several branches. The leaves are broadly oval and 6-12 cm long. They have a long slender tip. The base is wedge shaped. There are rounded teeth along the edge. The flowers are white but turn pink. They are 15-25 mm across. They occur in small clusters. The fruit are 25-30 mm long. The skin is thick and red. The flesh is yellow and juicy and sour.