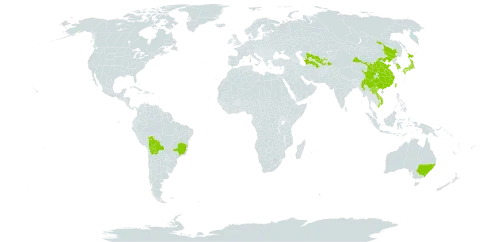
Trees 9–12 m tall; branchlets, petioles, pedicels, outside base of hypanthium glabrous or densely pubescent. Branches purplish brown to reddish brown; branchlets yellowish red. Winter buds purplish red, usually glabrous or rarely hairy at scale margins. Stipules linear, margin glandular, apex acuminate. Petiole 1–2 cm, apex with 2 nectaries; leaf blade oblong-obovate, narrowly elliptic, or rarely oblong-ovate, 6–8(–12) × 3–5 cm, adaxially dark green and lustrous, base cuneate, margin doubly crenate and often mixed with simple gland-tipped teeth when young, apex acute to shortly caudate; secondary veins 6 or 7 on either side of midvein, not extending to leaf margin. Flowers usually 3 in a fascicle, 1.5–2.2 cm in diam. Pedicel 1–1.5 cm. Sepals oblong-ovate, ca. 5 mm, outside glabrous, margin loosely serrate, apex acute to obtuse. Petals white, oblong-obovate, base cuneate, margin erose near apex. Ovary glabrous. Stigma disc-shaped. Drupe yellow or red, sometimes green or purple, globose, ovoid, or conical, 3.5–5 cm in diam., to 7 cm in diam. in horticultural forms, glaucous; endocarp ovoid to oblong, rugose. Fl. Apr, fr. Jul–Aug.
More
A small tree. It grows 9 m high and spreads 8 m wide. It loses its leaves during the year. The new shoots are red. The leaves are green. There are blunt teeth along the edge. The flowers are in pairs or small clusters. They are white. The fruit is about 3-5 cm across. They are reddish. They are juicy when ripe.
The fruit are eaten raw. They can be dried, canned stewed and made into jams, jellies, puddings, cakes, and sauces. Some varieties are used in cooking. They are brewed into wine.