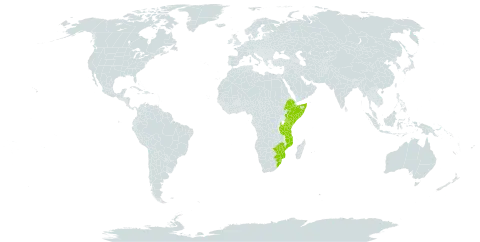
Several trailing or twining stems from a perennial tuberous root-stock; stems olive green, hispid. Leaf-lamina 7-9 x 5-7 cm, very variable in shape, ovate-triangular to subpentagonal, subentire to deeply 3-5(7)-lobed, lobes rounded or subacute and mucronulate, deeply cordate to sagittate-cordate at the base, hirsute above, densely hirsute below, basal nerves 3-5(7)-palmate, secondary nerves mostly ending in well-marked ovoid hydathodes (1 mm long with annular edge); petiole 4-6 cm long. Inflorescences pedunculate, borne at the nodes and appearing before the often abortive subtending leaves; peduncles hispid. Male spikes 3-4 cm long, very dense, on slender peduncles 4-12 cm long; flowers numerous, sessile, subtended by bracteoles. Female spikes 1-1.5 cm long, subcapitate; flowers fewer, sessile; rhachis bracteolate. Fruits 1.8-2 x 1.1-1.3 x 0.6-0.8 cm, yellow-orange at maturity, hirsute, crowded in spikes up to 6 cm long and 3.5 cm broad, on robust peduncles up to 2.5 cm long.
A climbing shrub. It has several trailing or twining stems. There is a tuberous rootstock. The leaf stalk is 4-6 cm long. The leaves are triangle shaped or 8 sided in outline. They can have 3-5 lobes. The base is heart shaped. The flowers are at the nodes. The male flowers are in 3-4 cm long spikes and the female flowers are in 1-1.5 flattened groups. There are many male flowers and fewer female flowers. The fruit are yellow to orange when ripe.
Leaf-lamina 7–9 × 5–7 cm., very variable in shape, ovate-triangular to subpentagonal, subentire to deeply 3–5 (7)-lobed, lobes rounded or subacute and mucronulate, deeply cordate to sagittate-cordate at the base, hirsute above, densely hirsute below, basal nerves 3–5 (7)-palmate, secondary nerves mostly ending in well-marked ovoid hydathodes (1 mm. long with annular edge); petiole 4–6 cm. long.
Fruits 1·8–2 × 1·1–1·3 × 0·6–0·8 cm., yellow-orange at maturity, hirsute, crowded in spikes up to 6 cm. long and 3·5 cm. broad, on robust peduncles up to 2·5 cm. long.
Male spikes 3–4 cm. long, very dense, on slender peduncles 4–12 cm. long; flowers numerous, sessile, subtended by bracteoles.
Inflorescences pedunculate, borne at the nodes and appearing before the often abortive subtending leaves; peduncles hispid.
Several trailing or twining stems from a perennial tuberous root-stock; stems olive green, hispid.
Female spikes 1–1·5 cm. long, subcapitate; flowers fewer, sessile; rhachis bracteolate.