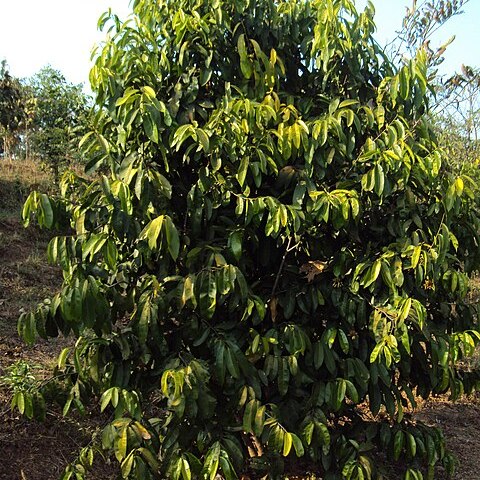
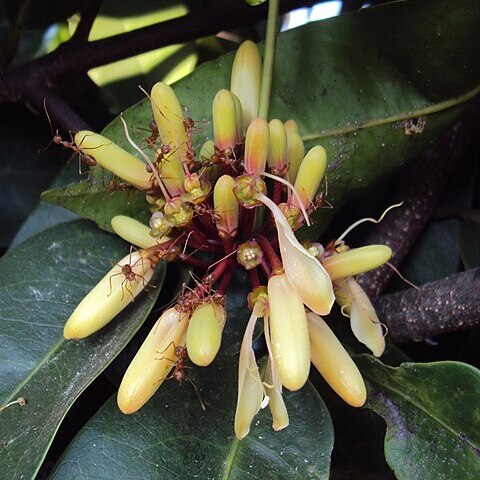
Glabrous evergreen shrub or tree, up to 20 m. Branchlets with a small pith, the base of each shoot provided with some stiff persistent scales. Leaves elliptic-oblong to lanceolate, rather acute or sometimes rounded or even subcordate at the base, blunt, more or less acuminate or sometimes rounded at the apex, 12-30 by 4-12 cm, midrib, nerves, and distinctly reticulated veins conspicuously prominent at either surface, always with internerval veins, usually with 2 pitted glands at the base beneath and similar ones scattered on the surface, less so above; petiole 1-2.5 cm. Flowers up to 20 or more in an umbelliform, glabrous or puberulous inflorescence. Peduncle more or less flattened, thickened at apex, terminal or axillary, sometimes on old wood, 1-30 cm. Pedicels jointed in the lower half, 0.5-2.5 cm, growing during anthesis, in fruit to more than 3 cm. Bracts minute. Calyx 4-lobed, 2-3 mm high, lobes about as long as the tube or longer, ± semiorbicular, puberulous outside. Petals 4, free, dorsally puberulous, obtuse, usually narrowed to the base, growing during anthesis, creamy-green to violet, purplish or brownish, up to 3 by 1 cm. Filaments puberulous, hairy except towards the apex, up to 2.5 cm, inserted at the base of the disk; anthers lanceolate to oblong, c. 4 by 1-2 mm. Disk glabrous or nearly so, c. 2 by 1.5 mm. Carpels 4, free, more or less puberulous, c. 2 by 2 mm; styles up to 2 cm. Fruits 1-4 together, flattened, with ± straight inner and ± semicircular outer margin, which is sharp and thinner in the upper half, the apex more or less overtopping the subapical stylar scar, 4-9 by 2½-5 cm; pericarp with similar glands as the leaf. Seed with an apical plumule and an adaxial conspicuous chalaza; testa thin; endosperm none; cotyledons planoconvex, up to 3.5 by 2.5 cm.
More
Tree to 10 m; trunk irregularly angled; branches glabrous.. Leaves simple, elliptic, ovate or obovate, 5–25 cm long, 2–8.5 cm wide, rounded to acuminate at apex, rounded or obtuse at base, glabrous, glandular beneath, densely reticulate-veined; petiole 7–15(–30) mm, often curved.. Inflorescence axillary, pendulous, with a thin peduncle 1–30 cm long and a terminal umbel of 4–13 flowers; bracteoles ± 1 mm; pedicel 10–30 mm.. Flowers white, bisexual.. Calyx of 4 obtuse sepals 6 mm long, 2 mm wide, with a concave gland in the centre.. Petals 4, contorted or imbricate in bud, 10–25 mm long, 9 mm wide, obtuse, pubescent outside.. Disc large.. Stamens 8, to 16 mm long.. Style with terminal, inconspicuous stigma.. Fruit of 1–4 carpels, each a woody drupe, ellipsoid with an unilateral thin wing in the upper part, 4–5 cm long, laterally compressed, 2.5–3.7 cm wide and 1.3–1.9 cm thick, 1-seeded.
A tree. It grows 21 m tall. The trunk is 39 cm across. The leaves are alternate and simple. The flowers are yellow to red and about 5 cm across. They are in small heads. The fruit are 6 cm long and purple-red. They are flattened and fleshy with one stone and 1-4 seeds inside. It has a thin wing.
Usually very rare, but locally rather common in the eastern part of its area, preferably in wet places in lowland, forests below 150 m, sometimes in localities which are periodically inundated by fresh or by salt water, for example on edge of the mangrove, in East North Borneo common in young swamp forests back of the mangrove. Fl. fr. Jan.-Dec.
More
A tropical plant. It grows in tidal swamps. It occurs up to 200 m above sea level. It can be on sandy soils or limestone.
Uses. In Sarawak the wood is used for making handles of knives, in the Solomons the macerated leaves, mixed with coconut oil, are applied to hair for cleansing purposes.The seeds are given as an emetic and purgative, and sometimes in bilious fevers. In the Philippines chips of wood are put in coconut oil which is drunk as a purgative. The same oil is used as a liniment for rheumatism and bruises. The plant is also used against malignant fevers, as a tonic, and as insecticide, specially against ants.The seeds contain oil to the extent of one third of their weight, but by difficulty of getting a sufficient supply it is not commercial ( GRESHOFF Schets. 1 1894 19 HEYNE Nutt. Pl. 1927 869 BURK. Dict. 2 1935 1945 Quis. Medic. Pl. Philip. 1951 475 ).
More
CAUTION: The seeds cause vomiting and diarrhoea.