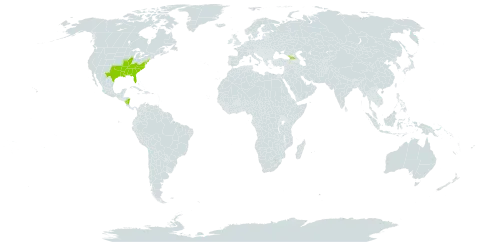
Tree to 25 m; bark gray to black, smooth when young, roughened with scaly ridges in age; twigs soon glabrous; buds thinly pubescent, 3–6 mm; lvs cuneate-obovate or cuneate-spatulate and abruptly widened above, entire or shallowly and irregularly 2–5-lobed, 4–10 × 1.5–5 cm, scarcely bristle-tipped, long-cuneate to the base, glabrous and dull green on both sides, or with some stellate hairs on the vein-axils; acorns 1–1.5 cm, the cup saucer-shaped, with numerous narrow, closely appressed scales, covering a third of the nut. Usually in damp or wet soil; Cape May Co., N.J. to Fla. and Tex., chiefly on and near the coastal plain, and n. in the interior to se. Mo.
A medium sized tree. It grows 15 m high and spreads 12 m across. It loses its leaves during the year. It has a broad-domed crown. The bark is dark grey and develops scaly ridges. The leaves are on slender stalks. The leaves are egg shaped but have lobes. They are glossy and deep green. The fruit are acorns enclosed in shallow cups.