Shrubs small, 1–2 m tall. Branchlets spreading, robust, glabrous; prickles abundant, yellow, straight or curved, to 8 mm, firm, flat, widening to a broad elliptic base. Leaves including petiole 3–5 cm; stipules mostly adnate to petiole, free parts lanceolate, glandular serrate; rachis and petiole glandular when young; leaflets 5–7(–9), suborbicular, obovate, or oblong, 8–15 × 5–10 mm, leathery, glabrous or abaxially along veins sparsely pubescent, base broadly cuneate or subrounded, margin 4–6-serrate at upper part, entire below, apex rounded-obtuse. Flower solitary, or 2 or 3 and fasciculate, axillary, 3–5 cm in diam.; pedicel 1–3.5 cm, usually glabrous; bracts absent. Hypanthium globose or ovoid, abaxially glabrous. Sepals 5, lanceolate, ca. 2 × as long as hypanthium, adaxially pubescent, margin entire, apex acuminate. Petals 5, yellow, obovate, base cuneate, apex emarginate. Styles free, shorter than stamens, slightly exserted, yellowish white villous. Hip dark red or purple-brown, globose or ovoid, ca. 1 cm in diam. shiny, with persistent, erect sepals; pedicel 1–3.5 cm, usually glabrous. Fl. May–Aug, fr. Aug–Nov. 2n = 14*.
More
A shrub. It grows 1-2 m high. The bark is reddish. The thorns are prominent and have a straight tip but are widened at the base. The leaves are compound with 5-9 round leaflets. These have a few large teeth There are some soft hairs underneath. The flowers are yellow and occur singly. The flower stalks are 1.5-4 cm long. The fruit are black to violet and 1-2 cm across.
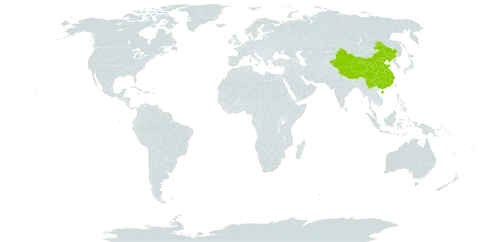
It is a cold temperate plant. In Kazakhstan it grows in foothills and gorges. It can grow in areas with a fairly low rainfall. In western China it grows between 1,100-1,800 m above sea level.