Shrubs, 2-4(-8) m, (sometimes forming clones by stem fragmentation). Stems: branches dark red-brown or yellow-brown, not to strongly glaucous, villous to glabrescent, (peeled wood smooth or striate, striae sometimes very dense, to 10 mm); branchlets yellowish, red-brown, or yellow-brown, or dark brown, moderately densely velvety, velutinous, or tomentose to glabrescent. Leaves: stipules rudimentary on early ones, foliaceous on late ones, (0.8-12.5 mm), apex acute to acuminate; petiole convex to flat adaxially, 6-17 mm, tomentose adaxially; largest medial blade narrowly elliptic, elliptic, oblanceolate, or obovate, 30-80(-135) × 12-33 mm, (2.3-)3-3.5(-4.5) times as long as wide, base convex or cuneate, margins flat, crenate, irregularly toothed, sinuate, or entire, apex acute, convex, or acuminate, abaxial surface glaucous, glabrous, pilose, sparsely pubescent or long-silky, midrib glabrous or densely pubescent, hairs (white, sometimes also ferruginous), wavy, adaxial dull or slightly glossy, glabrous or pilose, (hairs rarely ferruginous); proximal blade margins entire or serrulate; juvenile blade reddish or yellowish green, pilose, tomentose or moderately densely short-silky abaxially, hairs white and ferruginous. Catkins flowering before leaves emerge; staminate stout or subglobose, 23-52 × 12-22 mm, flowering branchlet 0-3 mm; pistillate densely flowered (loose in fruit), slender or stout, 25-108(-135 in fruit) × 12-33 mm, flowering branchlet 0-10 mm; floral bract brown, black, or bicolor, 1.4-2.5 mm, apex acute or convex, abaxially hairy, hairs straight. Staminate flowers: adaxial nectary oblong, 0.6-1.1 mm; filaments distinct, glabrous or hairy basally; anthers yellow or purple turning yellow, ellipsoid or short-or long-cylindrical, 0.5-1 mm. Pistillate flowers: adaxial nectary oblong or ovate, 0.7-1.3 mm, shorter than stipe; stipe 1.6-2.7 mm; ovary obclavate or pyriform, short-silky (hairs straight), beak sometimes slightly bulged below styles; ovules 6-16 per ovary; styles 0.3-1 mm; stigmas slenderly or broadly cylindrical, 0.48-0.64-0.88 mm. Capsules 6-11 mm. 2n = 76, 95, 114.
More
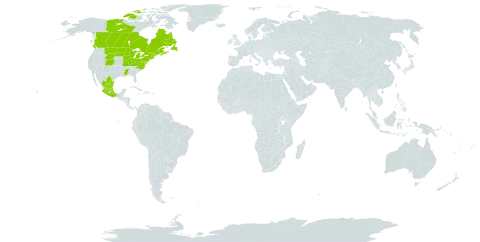
Few-stemmed shrub or small tree 2–5(–7) m; twigs rather stout, reddish to dark brown, hairy when young, usually later glabrate; buds large, to 1 cm; stipules small to large, rounded to semi-ovate; lvs mostly elliptic or elliptic-oblanceolate, 4–8(–10) × 1.5–3.5(–5) cm, acute or shortly acuminate, subentire to undulate-crenate, with flat margins, at maturity generally dark green and glabrous (seldom puberulent) above, the lower lf-surface becoming glaucous, generally reddish-strigillose when young, sometimes more persistently so, varying to loosely and persistently hairy; catkins precocious, sessile or nearly so, bractless or few-bracted, stout, and staminate 2–4 cm, ornamental, the pistillate 4–8(10) cm in fr; scales 1.5–2.5 mm, dark brown, long-villous; stamens 2; frs lanceolate, beaked, 7–10(–12) mm, densely gray-hairy; pedicels 1.5–3 mm; style 0.5–0.7 mm, the stigmas at least as long; 2n=76, 95, 114. Common in swamps and wet ground; Nf. to Alta., s. to Del., Ky., Mo., S.D., and Mont. S.×conifera Wangenh. is probably a hybrid with no. 24 [Salix humilis Marshall].
A shrub or tree. It grows 2-6 m tall. The leaves are 14 cm long and narrowly oval.