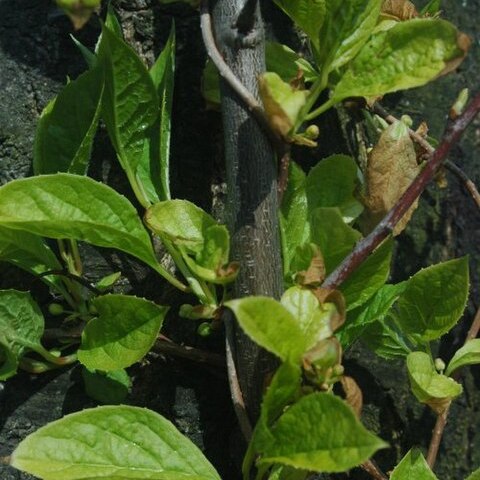
A deciduous creeper. It grows 6-9 m long. It spreads 6 m wide. The young stems are red. The leaves are rounded. They are large and light green. The flowers are small and white. They droop in clusters. Plants are separately male and female. The fruits are fleshy and red. They occur in long strings. These are 15 cm long.