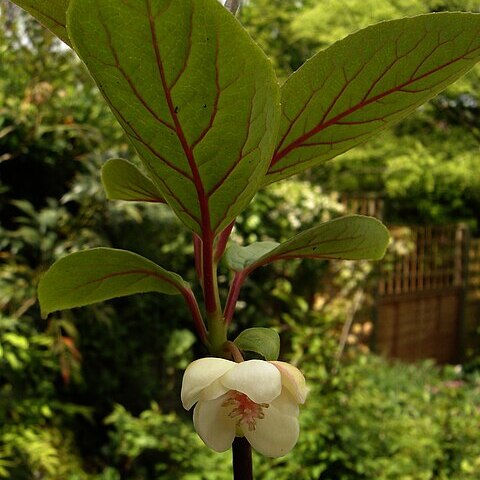
A trailing herb or climber. It can climb 6 m high. The leaves have stalks. They are alternate or clustered. The are oval or wider near the base. They are pointed. They have small teeth near the end. It loses its leaves during the year. Plants are separately male and female. The flowers have stalks. They are white and droop. The flowers have a scent. The fruit is round and red. It does not have a stalk. It is fleshy and with 2 seeds.