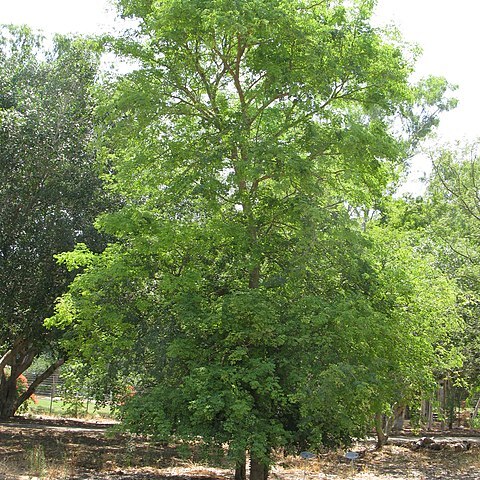
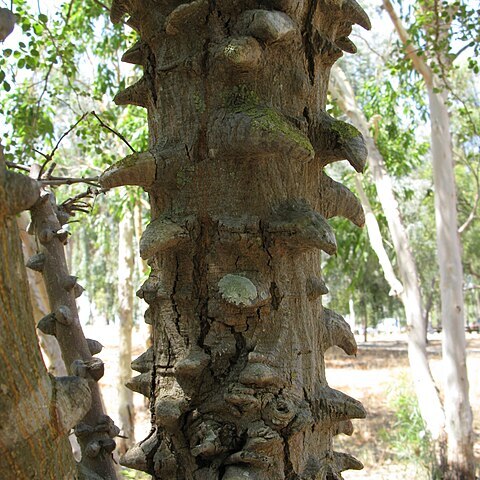
Tree to 30 m high; crown rounded or branches ascending and spreading slightly, often cylindrical in young plants; trunk to 0.75 m in diam., typically beset with persistent prickles arising from swollen knobs up to 6.3 cm long. Bark yellowish-, grey-or reddish-brown, sometimes almost black, rough, fissured; young branchlets yellowish-, grey-or reddish-brown to blackish, flaking minutely, glabrous to pubescent. Stipules not spinescent, in pairs, ± linear, 1-3 x 0.2-0.6 mm, soon deciduous. Prickles in pairs below the nodes, strongly recurved, often broad-based, grey-to reddish-brown or black, up to 7 mm long. Leaves: petiole 0.5-4.3 cm long, glabrous to pubescent, adaxial gland often absent, variable in position, 0.3-0.7 x 0.2-0.5 mm; rhachis 0.8-10.2 cm long, glabrous to pubescent, usually without a gland at the junction of each pinna pair; pinnae 2-4 pairs; rhachillae 0.3-3.7 cm long; leaflets 1-2(4) pairs per pinna, (6.5)10-30(50) x (5.3)7-30(49.8) mm, very variable in shape, obliquely obovate-orbicular to broadly obovate-elliptic, apex rounded and often emarginate, sub-coriaceous, venose, glabrous above and below or sparingly to densely appressed-pubescent above and/or below. Inflorescences spicate, fascicled, on short lateral branchlets, or occasionally solitary, sometimes crowded into a terminal raceme. Flowers yellowish-white, sessile; spikes 1-10.2 cm long; peduncles 0.3-2.4 cm long, glabrous or subglabrous, occasionally pubescent. Calyx often tinged with pink or distinctly pinkish-red, glabrous, tube 0.7-1.75 mm long, lobes 0.3-0.8 mm long. Corolla glabrous, tube 1.5-2 mm long, lobes up to 0.75 mm long. Stamen-filaments free, up to 6 mm long; anthers 0.1 mm across, with a deciduous apical gland. Ovary glabrous, 0.6-1.5 mm long, very shortly stipitate. Pods olive-or dark-brown to blackish, 6.1-17.8 x 1.4-2.4(2.7) cm, oblong, straight or nearly so, acuminate apically, longitudinally dehiscent, glabrous, coriaceous, brittle, scarcely venose. Seeds olive to olive-brown, 10-13 x 10-13 mm, subcircular-lenticular, compressed; areole 6-8 x 6-8 mm, horseshoe shaped.
More
A tree. It has knobs on the trunk. These have hooks. The tree grows 18-25 m high. It loses its leaves during the year. The leaflets are roundish and the leaves are twice divided. There are 3-4 pairs of divisions (pinnae) with one or two pairs of leaflets on each. The leaflets are 2 cm long by 1.5 cm wide. There are small hooked thorns on the branches near the leaves. The flowers have a sweet scent. They appear before the leaves. The whole tree is covered with creamy-white flowers. They are in spikes 9 cm long. The fruit is an oblong pod. It is green but turns a dark black or brown. It splits open after it falls off the tree.
Tree, up to 30 m high. Trunk and larger branches usually with scattered irregularly shaped knobs. Prickles in pairs near nodes. Leaves with 2 or 3(4) pinnae pairs; leaflets 1 or 2 pairs per pinna, obovate or obliquely obovate, (7-) 12-50 mm wide. Inflorescences spicate, fascicled. Flowers yellowish white.