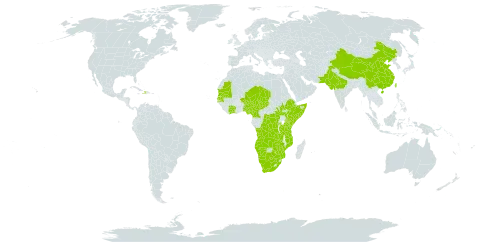
Shrub or tree up to 8 m high (in our area) with a slightly rounded or flattened and somewhat spreading crown, or a slender spindly tree with irregular virgate branches. Bark yellowish-or greyish-brown to purplish-black, rough, often corky and flaking off or smooth, papery and peeling off in strips; young branchlets yellowish-or greyish-brown to purplish-black, sometimes as though whitewashed over a purplish background, smooth or rough and flaking minutely or exfoliating to reveal a yellow inner layer, glabrous to densely pubescent. Stipules not spinescent, in pairs, linear, up to 5 mm long, soon deciduous. Prickles just below the nodes, up to 9 mm long, typically in threes, the central one hooked downwards and the two laterals ± curved upwards, or else solitary, the laterals being absent. Leaves: petiole 0.2-2 cm long, sparingly to densely pubescent, rarely subglabrous, adaxial gland usually present, sometimes two, variable in position, 0.5-0.75 mm in diam.; rhachis 0.7-6.9 cm long, sparingly to densely pubescent, lower surface with or without recurved prickles, with a gland at the junction of the top 1-5 pinnae pairs, between each pair or absent from some; pinnae (2)3-8(12) pairs; rhachillae 0.5-2.5 cm long, sparingly to densely pubescent; leaflets 7-25 pairs per pinna, 1-7 x 0.5-1.75 mm, linear to linear-or elliptic-oblong, apex obtuse to subacute, margins with or without cilia, sparingly appressed-pubescent above and beneath or entirely glabrous, lateral nerves invisible beneath or sometimes ± prominent. Inflorescences spicate, solitary or fascicled. Flowers yellowish-white, sessile; spikes 1.5-10 cm long, axis glabrous to densely pubescent; peduncle 0.1-2 cm long. Calyx sometimes tinged with pink, glabrous to somewhat pubescent, tube 0.9-2.6 mm long, lobes 0.2-0.8 mm long. Corolla glabrous or subglabrous, tube 2-3.2 mm long, lobes up to 0.9 mm long. Stamen-filaments free, up to 7 mm long; anthers 0.2-0.25 mm across, with a deciduous apical gland. Ovary glabrous, very shortly stipitate. Pods yellowish-or greyish-brown to brown, 1.8-9.5 x 1.2-3.4 cm, oblong, straight or almost so, longitudinally dehiscent, venose, apex rounded to acuminate or distinctly rostrate, sparingly to densely appressed-pubescent or puberulous. Seeds olive-brown to brown, 8-12 mm in diam., rbsubcircular-lenticular, compressed; central areole 2.5-6 x 2.5-5 mm, impressed, horseshoe shaped.
More
An evergreen shrub. It grows to 3-12 m high and 3 m across. The stem is erect. It is spiny and densely branched. The bark is waxy and smooth but then peels in yellow strips of a red base. The thorns are in threes. The central one is hooked and the two sides ones curve up and are brown to black. The leaves (phyllodes) occur one after the other along the branch and they are divided twice. The stalk is 7 cm long and it carries 3-6 pairs of side main leaflets. The flowers are yellow balls or spikes. They occur in stalked clusters in the angles where leaves join. The have a sweet smell. The pods are 10 cm long and 3 cm wide. They are thin and flat. They are yellow to light brown and papery. The veins are clear. They have few seeds. Probably now Senegalia senegal (L.) Willd.;