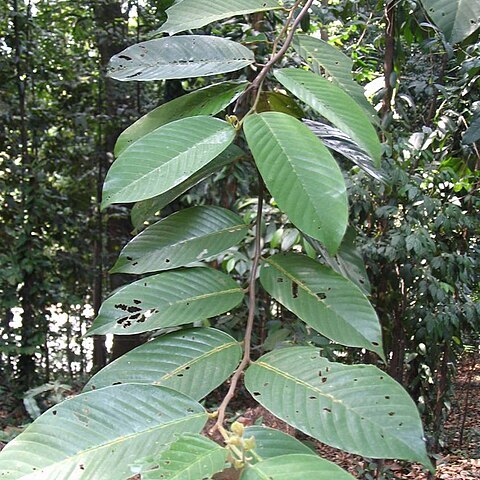
Large buttressed tree. Twig, panicle, leaf bud, stipule, petiole and nervation beneath persistently evenly densely shortly pale buff pubescent. Twig c. 1.5 mm ø apically, terete, ridged when young, much branched, slender, becoming glabrous, smooth; stipule scars short, horizontal, obscure. Bud 3-5 by 2-3 mm, compressed, broadly ovoid, subacute. Stipule to 10 by 3.5 mm, oblong to broadly hastate, obtuse, fugaceous. Leaves 8-14 by 3.5-5.5 cm, elliptic to ovate, thinly coriaceous, cream below in mature trees; base obtuse or broadly cuneate; acumen short, to 8 mm long; nerves 12-15 pairs, slender, curved towards margin, set at c. 40°-55°; tertiary nerves very slender, densely scalariform, obscure except in young trees; midrib narrow and depressed above and prominent beneath, in young trees beset from the base up more or less its length with lines of small, pale, scale-like domatia occasionally extending also on the nerves; petiole 1.0-1.5 cm long. Panicle to 14 cm long; terminal or axillary, terete, lax, slender, sparsely or densely evenly persistently pale brown to cream pubescent; regularly singly, rarely doubly, branched, branchlets short, bearing to 12 ± secund flowers; bracteoles to 3 by 2 mm, elliptic, obtuse, shortly pubescent, fugaceous. Flower bud to 6 by 3 mm, fusiform, subacute. Calyx densely pale brown pubescent outside, glabrous within; 3 outer lobes narrowly ovate, obtuse; 2 inner lobes broadly ovate, shorter, shortly acuminate. Petals pale yellow, narrowly oblong, densely pale yellowish grey pubescent on parts exposed in bud. Stamens 15, the inner 5 twice as long as the others and reaching half the length of the style; filaments long, tapering gradually; anthers subglobose; appendage to connective short, becoming reflexed. Ovary and stylopodium ovoid, glabrous; style filiform, twice as long as ovary and stylopodium, glabrous. Fruit calyx glabrescent or persistently shortly pubescent at base; 3 longer lobes to 10 by 2 cm, spatulate, obtuse, c. 5 mm broad above the to 8 by 6 mm thickened elliptic shallowly saccate base; 2 shorter lobes to 5.5 by 0.3 cm, unequal, similarly saccate at base. Nut to 2 by 1.3 cm, ovoid, densely pale buff pubescent; style remnant c. 2 mm long, tapering, acute.
More
It is a tall buttressed tree to 60 m.. Leaves oblong to elliptic, 7.5–15 × 3–8 cm., glabrous above, with fasciculate hairs on nerves and veins beneath and often domatia along the midrib in the lower lateral nerve-axils. Fruit with 3 long wings to 10 × 2 cm. and 2 short 5.5 × 0.3 cm.. Peter 10271! (E. Usambaras, Sigi valley, near Amani, 18 May 1915, 500 m.), a sterile specimen, is very similar to S. leprosula, but is undoubtedly not that species but the closely related S. platycarpa Heim, which has the leaves sparsely scabrid stellate-pubescent beneath rather than closely paletomentellous (or if only with scattered hairs then much smaller with rays reduced); the leaves are up to 17 × 8 cm., very slightly cordate at the base with midrib quite densely pubescent above. It is a native of the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, etc. The Peter specimen is exactly the same as Dupont 17 collected in the Seychelles and said to come from Java (where apparently S. platycarpa is not native but may probably be cultivated).
Can be grown by seedlings. Seeds needs soaking.