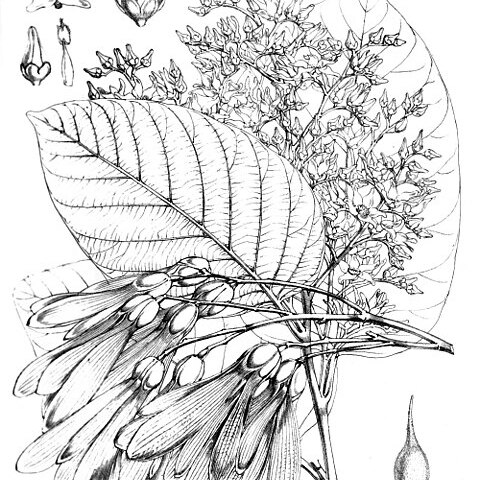
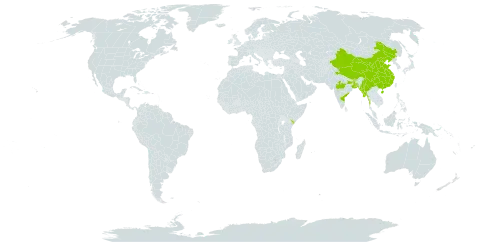
| Therapeutic use
|
Analgesics (bark), Anemia (bark), Anthelmintics (bark), Anti-bacterial agents (bark), Antipruritics (bark), Astringents (bark), Cough (bark), Diarrhea (bark), Dysentery (bark), Earache (bark), Epilepsy (bark), Gonorrhea (bark), Hemorrhage (bark), Hyperhidrosis (bark), Infection (bark), Insecticides (bark), Leprosy (bark), Leukorrhea (bark), Sialorrhea (bark), Tooth diseases (bark), Ulcer (bark), Wounds and injuries (bark), Astringents (flower), Diarrhea (flower), Dysentery (flower), Epilepsy (flower), Insecticides (flower), Sialorrhea (flower), Tooth diseases (flower), Aphrodisiacs (fruit), Diarrhea (fruit), Disorder of ejaculation (fruit), Pain (fruit), Skin diseases (fruit), Thirst (fruit), Ulcer (fruit), Analgesics (leaf), Anemia (leaf), Anthelmintics (leaf), Anti-bacterial agents (leaf), Antipruritics (leaf), Astringents (leaf), Cough (leaf), Diarrhea (leaf), Dysentery (leaf), Earache (leaf), Epilepsy (leaf), Gonorrhea (leaf), Hemorrhage (leaf), Hyperhidrosis (leaf), Infection (leaf), Insecticides (leaf), Leprosy (leaf), Leukorrhea (leaf), Sialorrhea (leaf), Tooth diseases (leaf), Ulcer (leaf), Wounds and injuries (leaf), Analgesics (plant exudate), Anti-bacterial agents (plant exudate), Anti-infective agents, local (plant exudate), Anti-inflammatory agents (plant exudate), Anti-obesity agents (plant exudate), Antipruritics (plant exudate), Aphrodisiacs (plant exudate), Appetite stimulants (plant exudate), Arthralgia (plant exudate), Asthma (plant exudate), Astringents (plant exudate), Bronchitis (plant exudate), Burns (plant exudate), Diarrhea (plant exudate), Digestive system diseases (plant exudate), Dysentery (plant exudate), Disorder of ejaculation (plant exudate), Expectorants (plant exudate), Eye burn (plant exudate), Eye diseases (plant exudate), Eye pain (plant exudate), Fever (plant exudate), Flatulence (plant exudate), Fractures, bone (plant exudate), Furunculosis (plant exudate), Gonorrhea (plant exudate), Headache (plant exudate), Hemorrhage (plant exudate), Herpes simplex (plant exudate), Hyperhidrosis (plant exudate), Menorrhagia (plant exudate), Neuralgia (plant exudate), Splenomegaly (plant exudate), Toothache (plant exudate), Tuberculosis (plant exudate), Tuberculosis, pulmonary (plant exudate), Ulcer (plant exudate), Wound healing (plant exudate), Wounds and injuries (plant exudate), Astringents (seed), Diarrhea (seed), Dysentery (seed), Epilepsy (seed), Insecticides (seed), Sialorrhea (seed), Tooth diseases (seed), Ache(Stomach) (unspecified), Aftosa (unspecified), Anodyne (unspecified), Anus (unspecified), Ardor (unspecified), Chest (unspecified), Colic (unspecified), Cosmetic (unspecified), Diarrhea (unspecified), Dysentery (unspecified), Dysuria (unspecified), Epididymitis (unspecified), Fever (unspecified), Fistula (unspecified), Gravel (unspecified), Hemiplegia (unspecified), Incense (unspecified), Ophthalmia (unspecified), Prolapse (unspecified), Skin (unspecified), Smallpox (unspecified), Soap (unspecified), Sore (unspecified), Spasm (unspecified), Tumor (unspecified), Whitlow (unspecified), Cancer (unspecified), Orchitis (unspecified), Tetanus (unspecified), Tubercle (unspecified), Anthrax (unspecified), Burn (unspecified), Carbuncle (unspecified), Hydrocoele (unspecified), Rinderpest (unspecified), Syphilis (unspecified), Chancre (unspecified), Anti-infective agents, local (unspecified), Skin diseases (unspecified), Abscess (wood), Anemia (wood), Burns (wood), Deafness (wood), Ear diseases (wood), Edema (wood), Fractures, bone (wood), Genital diseases, female (wood), Goiter (wood), Helminthiasis (wood), Hematologic diseases (wood), Leprosy, lepromatous (wood), Metabolism (wood), Anti-poisoning (wood), Pruritus (wood), Syphilis (wood), Ulcer (wood)
|