Trees. Branches verticillate and spreading. Leaves apically clustered, palmately 7-9-foliolate; stipules arrow-shaped, caducous; petiole 10-20 cm; leaflet blades elliptic-lanceolate, 10-15 × 3-5 cm, at first pilose, glabrescent when mature, base cuneate, margin entire, apex long acuminate or caudate. Inflorescence apical on branchlets, paniculate, erect, many-flowered. Pedicels shorter than flowers. Epicalyx lobes minute. Calyx purple-red, ca. 12 mm, divided nearly to base, lobes elliptic-lanceolate, abaxially yellowish brown pubescent, adaxially upper half white villous. Male flowers: stamens 12-15, capitate. Female flowers: carpels 5, hairy. Style curved; stigma 5-divided. Follicle ellipsoid and boat-shaped, 5-8 cm, woody, nearly glabrous, apex acute into beak, 10-15-seeded. Seeds black, ellipsoid, ca. 1.5 cm, smooth. Fl. Apr-May.
More
A medium sized tree. It grows to 10-20 m high. The tree has a straight trunk and branches to form a small crown. The bark is brown and flakes off. It loses its leaves during the year. The leaves are crowded at the ends of branches. They are compound and with 7 to 9 leaflets borne in a ring at the end of the leaf stalk. Each leaflet is 10-18 cm long by 3-5 cm wide. They have a pointed tip. The leaf stalk is 15-24 cm long and grooved. The flowers are strongly scented. They are red, dull yellow or purple. They are 2-4 cm wide in clusters 15-20 cm long and shaped like a pyramid. Male and female flowers are separate. The fruit are large, woody, nearly smooth and oval. They are 7.5-10 cm long and flattened. They turn red when ripe. The ripe fruit splits open showing large black seeds. The seeds are edible.
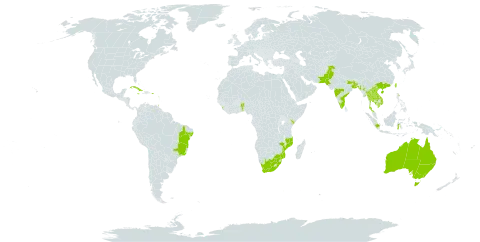
A tropical plant. Plants grow in the tropical lowlands in dry woodlands. They are common throughout the islands of the Philippines along the seashores and partly open forests at low and medium altitudes. In Nepal it grows up to 300 m altitude. It can grow in arid places. It suits hardiness zones 10-12.
More
Lowland dry woodlands. Primary and secondary forests, usually on river banks and sandstone rocks along the coasts, and in thickets and open areas, at elevations up to 1,000 metres.
The seed kernels are eaten raw. They can also be roasted like chestnuts. They can be soaked to remove the skins before roasting. The seeds can be used for oil. CAUTION: The seeds eaten in large numbers can cause diarrhoea and headaches. They probably should be cooked well. Immature seeds are not eaten. The rootstock of the young plant can be eaten raw. The leaves are used for food.