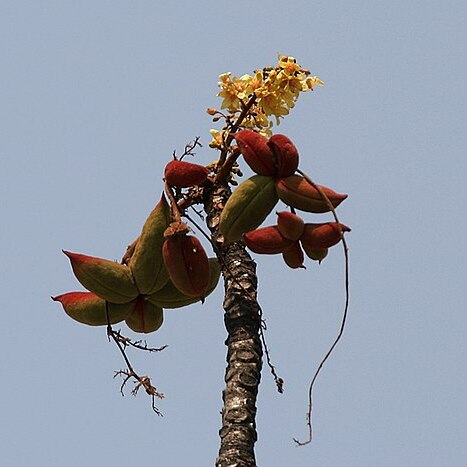
Trees; bark gray-white. Branchlets robust, with leaf scars, brown stellate pubescent when young. Leaves simple; stipules lanceolate, ca. 1 cm; petiole robust, ca. 16 cm, pilose; leaf blade palmately 3-7-lobed, 17-22 cm, abaxially densely yellow-brown stellate tomentose, adaxially sparsely pubescent, base broadly cordate, central lobe broadly ovate, ca. 8 × 8 cm at base, apex caudate. Inflorescence subterminal on branchlets, paniculate, densely ferruginous stellate tomentose. Calyx yellow, campanulate, ca. 1 cm, tube ca. 4 mm, abaxially pubescent, adaxially glabrous, lobes lanceolate, apex acuminate, ca. 6 mm, spreading outward. Male flowers: androgynophore curved, glabrous. Stamens 10. Female flowers: ovary globose. Style curved downward, hairy. Follicles narrowly ellipsoid, 3-5 cm, both surfaces densely ferruginous villous, apex shortly beaked. Seeds black, oblong. Fl. Feb, fr. Apr-Oct.
More
A tree that loses its leaves. It grows to 10 m high. The leaves have long stalks. The leaves are 30-48 cm long. They are heart shaped with 5-7 deep lobes. Young leaves are red and leaves are crowded near the top of the tree. There are star like hairs above and straight hairs underneath. The flowers are stalked. They are yellow in rusty hairy flower arrangements.
Mixed forests in gullies, also cultivated near villages; at elevations from 500-1,500 metres in southern China.
More
It is a tropical plant. In Nepal it grows between 300-600 m altitude. It grows in open places. In XTBG Yunnan.