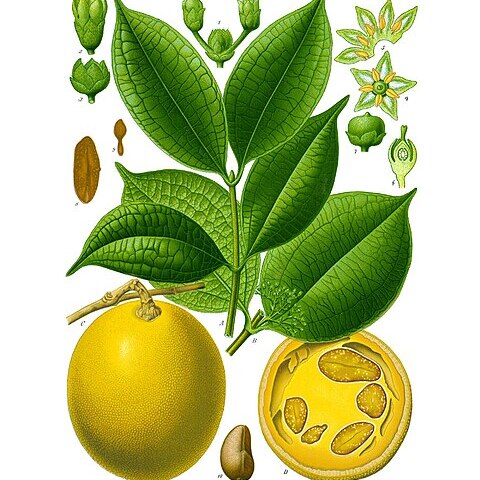
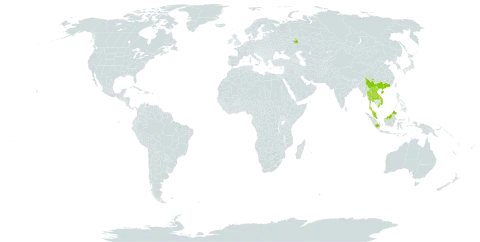
Lianas to 20 m. Branches grayish brown, lenticellate, glabrous; branchlets usually with 3--7 cm axillary simple tendrils. Petiole 7--10 mm; leaf blade ovate to elliptic, 6--17 X 3.5--7 cm, papery to leathery, glabrous and shiny, base obtuse to rounded, apex acute to acuminate, basal veins 3--5, reticulate veins present. Thyrses axillary, 2.5--3 cm, 10--20-flowered, minutely pubescent. Flowers fragrant, 5-merous. Calyx lobes ovate, ca. 1 mm, outside pubescent. Corolla yellowish, salverform, 1.5--1.7 cm, papillose; tube outside glabrous, inside with long woolly hairs basally, ca. 3 X as long as lobes; lobes oblong to elliptic, 4--5 mm, apex slightly thickened. Stamens inserted at corolla mouth; filaments very short; anthers oblong, 1.2--1.8 mm, glabrous, base shallowly 2-cleft, connectives apiculate at apex. Pistil ca. 1.5 cm. Ovary ovoid, ca. 1 mm. Style ca. 1.4 cm; stigma capitate. Berries orange when ripe, globose, 4--10 cm in diam.; pericarp to 5 mm thick, hard, woody, smooth, glabrous; 1--15-seeded. Seeds ovate, flat, 2--2.5 X 1.5--1.8 cm, with sericeous hairs. Fl. Apr-Jun.
A creeper. The stems are 20 m long. The branches are greyish-brown. They have tendrils. The leaves are narrowly oval and 6-17 cm long by 4-7 cm wide. They taper to the tip. The flowers are in groups of 10-20 flowers in the axils of leaves. The flowers have 5 parts and have a scent. The fruit are round berries, yellow when ripe. They are 4-10 cm across. They have a hard woody case. There are 1-15 seeds. These are oval and flat. They are 2-2.5 cm long by 1.5-1.8 cm wide.