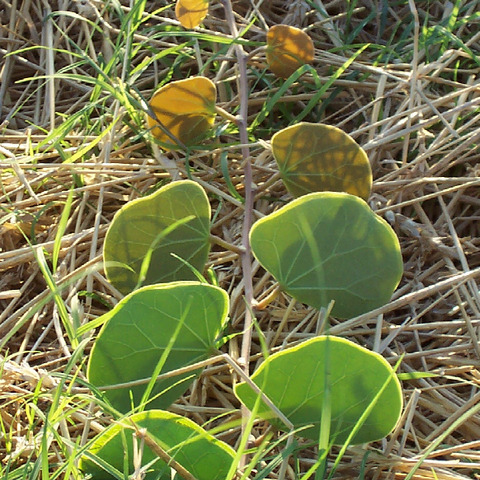
A herb or shrub. It is climbing and keeps growing from year to year. It has tuberous roots. The stem lie along the ground. They can be 6 m long. The lower parts can be woody. There are forked tendrils 1-4 cm long. The leaves are simple and arranged alternately. The leaf blade has 2 lobes. These are kidney shaped and 4-5 cm long by 5-6 cm wide. The flowers are in groups 16 cm long and at the sides. The flowers contain both sexes and are yellow turning red with age. The fruit is a oval pod 4-6 cm long by 3-4 cm wide and flattened. It is woody and usually has 1-2 seeds. The pod is constricted between the seeds. The seeds are round or oval and 2-2.5 cm long by about 1.5 cm wide. They are reddish-brown.
Herb with prostrate and trailing stems up to 3 m long. Leaf lobes reniform, 30-75 mm long, leaves divided apically for more than half of their length, petiole 30-70 mm long. Pods oval, 35-60 x 28-40 mm. Flowers yellow.
Racemes 4–12 cm long, c.8–20-flowered, rather shortly pedunculate; bracts 3–4 mm long, linear-lanceolate; bracteoles on the pedicel, a little smaller; pedicels 2–4.5 cm long.
Leaves: petiole 1.5–3.5 cm long; lamina 3–7.5 × 4–10 cm, bilobed halfway or more, cordate at the base, the lobes reniform; stipules 3–5 mm long, elliptic-oblong to obovate.
Petals yellow, the 4 larger ones 1.5–2.5 cm long, obovate above a long claw, slighly crinkled.
Sepals 8–12 mm mm long, oblong-lanceolate, tapered distally, pubescent, the upper pair fused.
Stamens: filaments of fertile stamens 10–12 mm long, those of stamonodes 3–6 mm long.
Pod red turning brown, shortly stipitate, 5–9 × 4.5–6.5 cm, ovate-oblong, glabrous.
Stems prostrate and trailing up to several metres long, herbaceous or woody below.
Seeds brown to brownish-black, 1.3–2 × 1.2–1.8 cm, ovoid to subspherical.
Branches reddish to greyish pubescent at first, glabrescent.
Ovary 5–6 mm long, glabrous or nearly so.
Tendrils forked, 1–4 cm long.