Tree to 15 m high or a small shrub or bush, crown typically flattened and spreading, sometimes rounded; trunk to 1 m in diam. Bark grey to grey-brown or blackish, at times reddish-brown, rough, fissured, seldom ± smooth; young branchlets greyish-to reddish-brown or purplish-black, glabrous to densely pubescent, lenticellate, often flaking minutely. Stipules spinescent, some short, hooked and up to 5 mm long, mixed with other long straight slender whitish spines 1.5-10 cm long; 'ant-galls' and other prickles absent. Leaves: petiole 0.2-0.8(1.4) cm long, sparingly to densely pubescent, adaxial gland usually present and just below lowest pinna pair; rhachis 0.2-2(4.6) cm long, sparingly to densely pubescent, eglandular or sparingly glandular, a small gland often present at the junction of the top 1-3 and lowest 1-2 pinnae pairs or absent from some, variable; pinnae 2-10(14) pairs; rhachillae 0.3-1.7 cm long, sparingly to densely pubescent; leaflets 6-22 pairs per pinna, 1-4 x 0.6-1 mm, linear to linear-oblong, apex rounded to acute, glabrous or sparingly to densely appressed-pubescent beneath and sometimes also above, indumentum often concentrated along midrib beneath, margins with or without cilia. Inflorescences capitate, on axillary peduncles, fascicled or solitary. Flowers white to pale yellowish-white, sessile; peduncles 0.4-2.4 cm long, sparingly to densely pubescent; involucel in lower third of peduncle. Calyx glabrous except for the lobes which are sparingly to densely pubescent, tube 0.9-1.6 mm long, lobes up to 0.8 mm long. Corolla glabrous throughout or apices of lobes sparingly to densely pubescent, tube 1.2-2 mm long, lobes up to 1 mm long. Stamen-filaments free, up to 4.5 mm long; anthers with a deciduous apical gland. Ovary glabrous, up to 1.5 mm long, shortly stipitate. Pods variously contorted or spirally twisted, 0.6-1.2 cm wide, greenish-yellow to olive-brown, longitudinally veined, indehiscent or very tardily dehiscent on the ground, usually glabrous but at times sparingly to densely pubescent, eglandular or with few to many minute scattered reddish glands. Seeds olive-to reddish-brown, 4-7 x 3-6 mm, elliptic to subcircular, smooth, compressed; areole 3-6 x 2-4 mm.
More
A flat topped shrub or tree. It grows to 4-21 m tall depending on rainfall. The crown occurs in layers. It is flat and spreading. The bark is grey brown and cracked when mature. It tends to shoot from the base rather than have a distinct trunk. It has two kinds of spines. Some are long and hooked and others are straight and long. The leaves are divided twice. There are 2-10 pairs of small leaflets. The stalk is only 2-4 cm long. The flowers are cream coloured round heads. The fruit are yellow to brown pods. These hang in dense bunches. The pods are twisted. Each pod has up to 10 brown seeds.
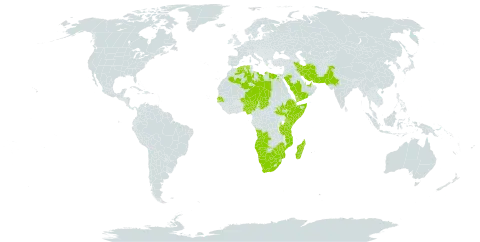
It grows in Mediterranean and tropical places. It is common all over Africa. It does best on alkaline soils. It grows in hot dry areas. Some forms have salt tolerance. It is drought resistant and cold tolerant. It grows between sea level and 2,000 m above sea level. It grows in areas with an annual rainfall between 50-1,000 mm. It can grow in arid places. It suits hardiness zones 9-11.
More
Widespread in the Sahel, in woodlands and in the savannah. It generally forms open, dry forests in pure stands or mixed with other species.