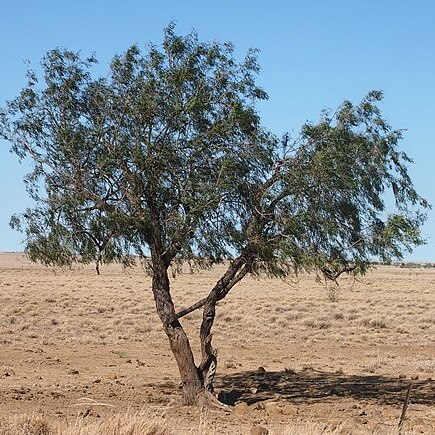
A tree. It grows 6-10 m high. It starts as a woody climber. It can be a shrub 4-5 m high. It can have one or several trunks. The crown is dense. The bark is rough and furrowed. The leaves are narrowly sword shaped. They are dark green and glossy. The leaves hang downwards. The flowers are small and cream coloured. The fruit are small and round. They are 3-4 mm across. They have a single long yellow wing.