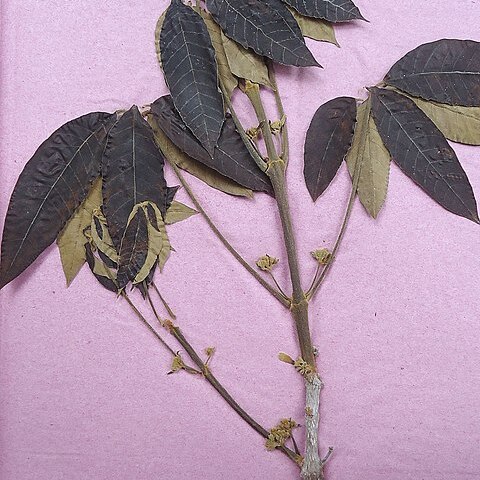
firmly chartaceous or rarely subcoriaceous when mature, very lightly and ob-scurely pulverulent-puberulent above when immature, usually glabrescent and shiny when mature, puberulent to short-tomentellous (sometimes very densely so) beneath when immature, less so when mature; petioles 2.5-15 cm long, densely puberulent or short-pubescent; petiolules 1-17 mm long when mature, densely puberulent, margined, the lateral petiolules usually shorter than the central ones, often obsolete on immature leaves. Inflorescences axillary, cymose, abundant, much shorter than the subtending petioles, 2-9.5 cm long and 1-10 cm wide, 1-4 times dichotomous with wide-spreading branches, usually flowering before the leaves are completely mature, whitish-or yellowish-puberulent throughout, the hairs denser at all the joints; peduncles 0.7-4.5 cm long, the cyme-branches con-spicuously flattened; pedicels 1-2 mm long; foliaceous bracts often present, simple, obovate-spatulate or oblong-elliptic, stipitate 1-1.5 cm long, similar to the im-mature leaflets in pubescence; bractlets linear, 1-4 mm long; prophylls setaceous, ca. 1 mm long. Flowers with the calyx campanulate, 2-3 mm long and 2-5 mm wide, densely puberulent, 5-dentate, the teeth ovate, obtuse or acute, often re-curved or reflexed, often nigrescent on the inner surface; corolla blue or pinkish-blue to violet, lilac, or purple, rarely white, hypocrateriform, the tube 6-7 mm long, puberulent outside above the calyx, the limb conspicuously 2-lipped, the 4 small lobes ca. 4 mm long and 2 mm wide, obtuse, the fifth lobe much enlarged, rounded, ca. 7 mm long and 8 mm wide, the margins crisped. Fruit succulent, purplish-or violet-black, 1.1-2 cm long and 0.9-1.5 cm wide, glabrous, edible; fruiting cymes usually 4-6.5 cm long and lax, the pedicels 1-5 mm long, strigose-pubescent; fruiting-calyx flattened-campanulate, ca. 5 mm long and 12 mm wide, shallow, coriaceous, dark, finely short-strigose outside, 4-or 5-lobed, the lobes broadly triangular-ovate and often more or less obscurely toothed.
More
Tree to 28 m tall; trunk to 60 cm in diameter 1.5 m above ground; branchlets gray to brownish, acutely or obtusely tetragonal, the pith small, the youngest parts densely puberulent with sordid-grayish or yellowish hairs. Leaves 3-7-foliolate, sometimes subopposite; leaflets usually unequal in size, the two lower-most usually considerably smaller, the central leaflet oblong or elliptic to oblan-ceolate-elliptic or obovate, rarely lanceoate, 4-23 cm long and 2.4-7.2 cm wide, apically acute to abruptly short-acuminate or even caudate-acuminate, the acumen itself blunt, basally acute or acuminate-attenuate, entire, green on both surfaces when mature or lighter beneath, brunnescent or nigrescent above when immature,
A tree. It grows 10-20 m high. The crown has a lot of leaves. The trunk is short and 50-90 cm across. The leaves are compound with leaflets spread out like fingers on a hand. The leaf stalks are 6-8 cm long. There are 5-7 leaflets of unequal size. The 2 near the base are smaller and 4-7 cm long while the others are 8-12 cm long. The flowers are in the axils of leaves. They are in groups 3-6 cm long and are purple. The fruit is round and fleshy. It is red or purple when ripe. It only has one seed.