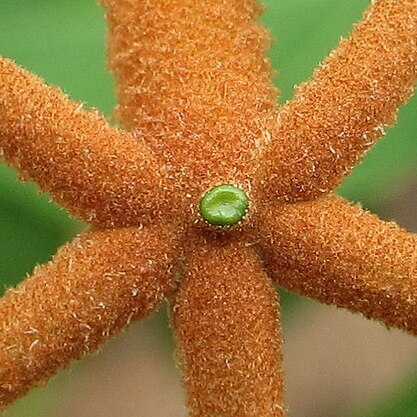
Many stemmed shrub 1.5-4.5 m tall often scandent, or small tree to 6(15) m tall, sometimes a liane, often deciduous; bark fissured, grey to light brown; older stems brownish-yellow, red and grey; young stems orange lanate. Leaves (3)5(7)-foliolate; petioles 2.5-12 cm long, terete; median petiolules (0.2)1.0-2.0(3.5) cm long; leaflets 2.5-11 x 1.5-4 cm, median leaflet largest, narrow to broadly lanceolate, acute to narrowly acuminate or sometimes short acuminate or rounded at the apex, cuneate or rounded at the base, glabrous on upper surface or with scattered small hairs, paler and densely finely hairy beneath, gland-dotted or not, entire or occasionally deeply toothed toward the apex, nerves sunken above and raised beneath. Inflorescences axillary, few to many-flowered, of ± sturdy short simple dichasia 2-4 cm long, orange-tawny tomentose; bracteoles 0.5-1.2 cm long, narrowly lanceolate. Calyx obconical, 5-lobed, ferruginous pubescent outside, gland-dotted, accrescent in fruit; tube 2-3 mm long; lobes (1)1.5-3 mm long, erect. Corolla creamy-white, c. 16 mm long, ferruginous pubescent outside, gland-dotted; tube to c. 7 mm long, curved; lobes mauve, at acute angle to tube, middle lower lobe 5-7 x 7-8 mm the others smaller. Stamens exserted from tube; filaments with glandular hairs. Ovary narrowly ovoid, not gland-dotted, lanate towards apex; apex long-acuminate; style c. 10 mm long. Drupe c. 3 x 2.5 cm, spherical-ellipsoid, rounded or sharp-tipped at the apex, not enclosed in the enlarged calyx, purplish-black at maturity; fruiting calyx saucer-shaped, pubescent, not gland-dotted.
More
A shrub or tree. Often it loses its leaves during the year. It can grow from 4 m tall to 13 m tall. The trunk is slightly fluted. The small branches have rusty brown hairs. The bark is smooth and light grey. It can have small grooves and small pieces flaking off with age. The leaves are compound with 3-7 leaflets arranged like the fingers on a hand. They occur opposite one another along the stem. The leaflets are unequal in size. The largest leaflet is 5-14 cm long with a long pointed tip. The upper surface is dull with a few hairs while the lower surface has rusty hairs and clear veins. The leaf stalk is 12 cm long while the leaflet stalks are 1 cm long. The flowers are in dense heads beside the leaves. The flower stalk is 5 cm long. The flowers are small and like tubes. They are 1 cm long and have one blue-violet lobe and four white petals. The fruit is rounded and fleshy. It is green with white spots. Fruit turn shiny black when ripe. They are 4 cm long and edible.
Shrub, 2.5-3.0(-9.0) m high. Leaves 5-7-pinnate, leaflets petiolate, adaxial surfaces sparsely soft-hairy, apex acute to acuminate. Calyx cup-shaped in fruit. Ovary densely hairy in upper half. Fruit fleshy. Flowers with white tube and pale purple lobes.
Shrub, 2.5-3.0 m high. Leaves 5-7-pinnate, leaflets petiolate, adaxial surfaces softly hairy, apex to a lesser extent acute, not acuminate. Calyx cup-shaped in fruit. Ovary densely hairy in upper half. Fruit fleshy.