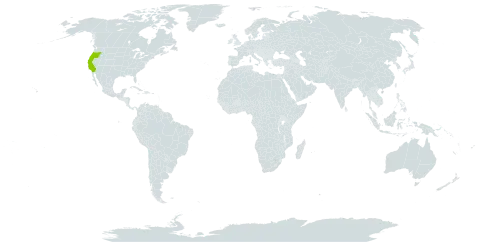
Moist stream borders, scrub and the edges of oak and pine woods in canyons and dry slopes below 1,200 metres.
| Life form | perennial | ||||||||||||
| Growth form | tree | ||||||||||||
| Growth support | free-standing | ||||||||||||
| Foliage retention | deciduous | ||||||||||||
| Sexuality | hermaphrodite | ||||||||||||
| Pollination | entomogamy | ||||||||||||
| Spread | - | ||||||||||||
| Mature width (meter) | 10.0 | ||||||||||||
| Mature height (meter) | 7.8 - 10.0 | ||||||||||||
| Root system | - | ||||||||||||
| Rooting depth (meter) | 0.9 | ||||||||||||
| Root diameter (meter) | - | ||||||||||||
| Flower color | |||||||||||||
| Blooming months |
|
||||||||||||
| Fruit color | |||||||||||||
| Fruiting months | - | ||||||||||||
| Nitrogen fixer | - | ||||||||||||
| Photosynthetic pathway | c3 |
| Light |
|
| Soil humidity | |
| Soil texture | |
| Soil acidity | |
| Soil nutriment | - |
| Hardiness (USDA) |
| Uses | forage material medicinal poison wood |
| Edible | fruits saps seeds |
| Therapeutic use | Toothache (bark), Hemorrhoid Remedy (fruit), Poison (fruit), Veterinary Aid (fruit), Hemorrhoid Remedy (seed), Poison (seed), Poison (unspecified) |
| Human toxicity | - |
| Animal toxicity | - |
| Mode | cuttings seedlings |
| Germination duration (days) | - |
| Germination temperacture (C°) | - |
| Germination luminosity | - |
| Germination treatment | soaking |
| Minimum temperature (C°) | -18 |
| Optimum temperature (C°) | - |
| Size | - |
| Vigor | - |
| Productivity | - |

| LSID | urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:781583-1 |
| WFO ID | wfo-0000522247 |
| COL ID | 65BYX |
| BDTFX ID | - |
| INPN ID | - |
| Wikipedia (EN) | Link |
| Wikipedia (FR) | Link |