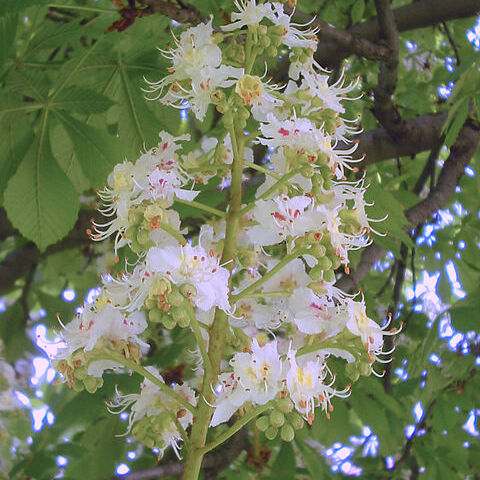
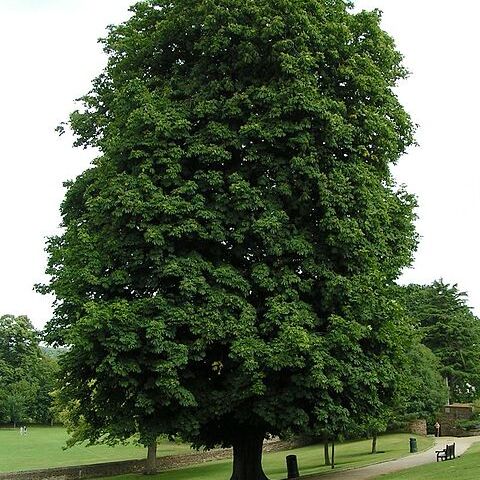
Deciduous trees or, less commonly, large shrubs, usually with large buds. Leaflets 5-7-(11). Infl. erect. Calyx always connate, tubular or campanulate, 5-toothed. Disc annular.
Sepals connate at least half their length to form a lobed tube; lvs deciduous, 5–11-foliolate. 13, N. Hemisphere.