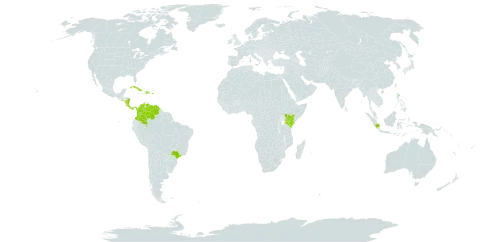
Moderate or large tree, the branchlets tomentose when young becoming gla-brous, moderately lenticellate, unarmed. Leaves moderately large, bipinnate, the pinnae 7-15 pairs opposite on the rachis, the leaflets 10-25 pairs per pinna; petioles mostly 2-3 cm. long, tomentulose, nearly terete, usually eglandular; primary rachis up to 10 cm. long, similar to the petiole, bearing at the apex at insertion of terminal pair of pinnae a sessile, subcupular gland; pinnular rachis 2-5 cm. long, puberulent, usually bearing a sessile gland at insertion of the terminal pair of leaflets; leaflets opposite, oblong-subfalcate, 4-6 mm. long and 1-2 mm. wide, asymmetrically acute apically, obliquely rounded or subtruncate basally, pubescent above and more heavily so below, somewhat paler below, the costa excentric, the venation obscure; stipules early caducous. Inflorescence of several pedunculate umbels from terminal and subterminal defoliate or minutely foliate nodes; peduncles slender, up to 3 cm. long, tomentulose; bractlets linear-spatulate, caducous. Flowers briefly pedicellate, dense; calyx narrowly obconic, about 2.5 mm. long, tomentulose; corolla narrowly funnelform, about 5 mm. long, tomentose, the lobes the length of the tube; stamens about 14 mm. long, the staminal tube well included; ovary glabrous. Legume broadly linear, 8-11 cm. long and almost 2 cm. wide, stipitate, pubescent, falsely septate, the seeds transverse.
Can be grown by seedlings. Seeds needs soaking.