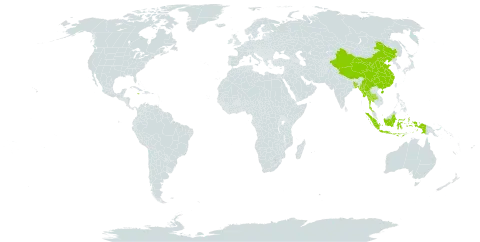
Pseudostems 1.5--3 m. Leaves sessile or subsessile; ligule orbicular, 4--6 mm, glabrous; leaf blade lanceolate or elliptic-lanceolate, 25--40 × 6--8 cm, glabrous, base and apex acute. Panicles erect, to 30 cm; branches expanded, 2--8 cm; rachis and branches tomentose, usually lax with remote cincinni; bracts ovate; bracteoles funnelform, tomentose, persistent. Pedicel 3--5 mm. Calyx tubular, 1.2--1.5 cm, split down 1 side for ca. 2/3 its length, pubescent abaxially. Corolla tube ca. 1 cm; lobes oblong, ca. 1.2 cm, pubescent abaxially, central one wider than lateral ones, apex cucullate. Lateral staminodes subulate. Labellum obovate, ca. 1.5 cm, base clawed, apex 2-cleft. Stamen ca. 1.5 cm; filament linear, ca. 1 cm; anther curved. Ovary densely pubescent. Capsule black when dry, globose, 1.2--1.5 cm in diam., sparsely pubescent, irregularly dehiscent, apex with flower remains; pedicel 5--10 mm. Seeds 5--6 mm in diam. Fl. and fr. Jul--Aug.
More
A ginger family plant. It is a herb. It can be 3-4 m high. It keeps growing from year to year. It has an aerial stem. The shoot and leaves have a scent. The leaves are large and in two rows. The flowers are white and have a scent. The fruit are capsules. They occur in clusters. They are green but turn black when ripe.
The rhizome is boiled with potato and made into a chutney. They are also eaten raw. The leaves are used to wrap food to provide an aroma. The young tender shoots and leaves are cooked and eaten as a vegetable. They are cooked with small fish or also eaten raw. The stem piths are eaten fried. The flowers are used as a spice. The harvested food can be stored for 5-6 days.